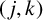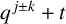5209 results
On the relevance of lift force modelling in turbulent wall flows with small inertial particles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2024, A47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Australian Banking and Finance Law and Regulation
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- July 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 July 2024
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Disease Burden attributable to High Body Mass Index in Belt and Road Initiative Countries, 1990-2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Posterior cingulate and medial prefrontal excitation-inhibition balance in euthymic bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variation in the structural order of kaolinite in regolith as an effective indicator of REE mineralization
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 72 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, e1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Choosing innovation alliance governance structure: The roles of performance feedback and top management team characteristics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
- Export citation
CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIALS OF THE MATRICES WITH
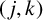 $(\,j,k)$-ENTRY
$(\,j,k)$-ENTRY 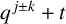 $q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
$q^{\,j\pm k}+t$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
The amino acid sensor MetRS is required for methionine-induced milk protein synthesis in a domestic pigeon model
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Addressing the Neurodevelopmental Impacts of Prenatal Substance Exposure: Insights from a Taiwanese Study on Methadone Maintenance Treatment During Pregnancy
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Evidence-Based Physiotherapeutic Interventions Enhancing Hand Dexterity, Activities of Daily Living and Quality of Life of Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Systematic Review
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
AI Approaches for the Discovery and Validation of Drug Targets
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Precision Medicine / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. 1-44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
High efficiency, high-resolution multiple monochromatic imaging based on multilayers mirrors array for laser-plasma diagnostic of X-ray continuum emission
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Source Data Verification (SDV) Quality in Clinical Research: A Scoping Review
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A study of streamline geometries in subsonic and supersonic regions of compressible flow fields
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, A26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Numerical modelling and analysis of porous surface-enhanced jet cooling using copper inverse opals in single-phase flow
-
- Journal:
- Flow: Applications of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 4 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2024, E9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shared and distinct electroencephalogram microstate abnormalities across schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Part I - Beyond Translingual Playfulness
-
- Book:
- Translingual Practices
- Published online:
- 07 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 May 2024, pp 17-102
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part IV - Ways Forward
-
- Book:
- Translingual Practices
- Published online:
- 07 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 May 2024, pp 219-246
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - Introduction
-
-
- Book:
- Translingual Practices
- Published online:
- 07 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 May 2024, pp 1-16
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part II - Online Activism
-
- Book:
- Translingual Practices
- Published online:
- 07 May 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 May 2024, pp 103-162
-
- Chapter
- Export citation