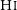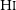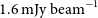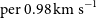254 results
B.6 Long-term risk of subsequent stroke after transient ischemic attack or minor stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
24 Associations Between Positive Psychological Factors and Neurocognitive Functioning in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 337
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Validation of a culturally sensitive, Swahili-translated instrument to assess suicide risk among adults living with HIV in Tanzania
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 10 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, e67
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Treatment of hypoplastic left heart syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2023, pp. 659-666
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of sedentary behavior and emotional support on prenatal psychological distress and birth outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, pp. 6792-6805
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An app a day: Results of pre- and post-surveys of knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) regarding antimicrobial stewardship principles among nurses who utilized a novel learning platform
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2023, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The estimation of environmental and genetic parental influences
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2022, pp. 1876-1886
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ten new insights in climate science 2022
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 5 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2022, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
What is Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorders in Republic of Georgia?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S232
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Applying the Semi-Automated MicroED Processing Pipeline, AutoMicroED
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 1084-1085
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Role of Nanoscale Coherent Precipitates in Microstructure Evolution of NiTi-based Shape Memory Alloys
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2354-2355
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Pharmacological and nonpharmacological approaches to reduce disinhibited behaviors in dementia: a systematic review
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2022, pp. 335-351
-
- Article
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Status and Direction of Atom Probe Analysis of Frozen Liquids
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2022, pp. 1150-1167
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plasma vitamin B12 concentration is positively associated with cognitive development in healthy Danish 3-year-old children: the SKOT cohort studies
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2021, pp. 1946-1954
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
2021 PACES expert consensus statement on the indications and management of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices in pediatric patients: Developed in collaboration with and endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Endorsed by the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), the Indian Heart Rhythm Society (IHRS), and the Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS).
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 11 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2021, pp. 1738-1769
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
2021 PACES expert consensus statement on the indications and management of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices in pediatric patients: executive summary: Developed in collaboration with and endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Endorsed by the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), the Indian Heart Rhythm Society (IHRS), and the Latin American Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS).
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 11 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 1717-1737
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rates of Cognitive and Functional Impairments in Older Adults Residing in a Continuing Care Senior Housing Community
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2021, pp. 62-73
-
- Article
- Export citation
Beyond artificial intelligence: exploring artificial wisdom
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 32 / Issue 8 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2020, pp. 993-1001
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Predictors of post-thyroidectomy hypocalcaemia: a systematic and narrative review
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 134 / Issue 6 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 541-552
- Print publication:
- June 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation