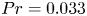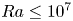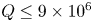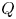186 results
Sedimentation rate changes across the Chinese Loess Plateau from luminescence dating of Malan loess in the Sanmen Gorge
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Adaptive integral terminal sliding mode control of unmanned bicycle via ELM and barrier function
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linguistic synesthesia detection: Leveraging culturally enriched linguistic features
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Processing ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Brain magnetic resonance imaging outperforms clinical severity ratings in the prediction of treatment outcomes in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, p. S85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A multivariate meta-analysis of peripheral cytokine levels in obsessive compulsive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, pp. S42-S43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Functional connectivity subtypes of MDD and their associations with gene expression profile, neurotransmitter, and cognition
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, p. S362
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Investigations on the turbulent
 ${\boldsymbol{/}}$non-turbulent interface in supersonic compressible plate turbulent boundary layer
${\boldsymbol{/}}$non-turbulent interface in supersonic compressible plate turbulent boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, A30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nef cones of fiber products and an application to the cone conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of horizontal magnetic fields on turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a cuboid vessel with aspect ratio Γ = 5
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Abnormal intrinsic brain functional network dynamics in first-episode drug-naïve adolescent major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 8 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 1758-1767
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Subducted oceanic slab break-off in a post-collisional setting: Constraints from petrogenesis of Late Carboniferous dykes in central West Junggar, Xinjiang, NW China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2023, pp. 1711-1741
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Theoretical analysis of the effect of doping with Na(I), K(I), Mg(II), Ca(II) and Fe(II) on the electronic and mechanical properties of pyrophyllite
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, pp. 113-120
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linked patterns of symptoms and cognition with brain controllability in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S420
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Swallow-tailed separation bubble on a low-aspect-ratio trapezoidal plate: effects of near-wall spanwise flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 965 / 25 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2023, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Population dynamics and conservation status of the white-headed langur in the Chongzuo forest fragments, Guangxi, China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pulse repetition-rate effect on the intensity inside a femtosecond laser filament in air
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late Permian to early Triassic gabbro in North Lhasa, Tibet: evidence for plume - subduction-zone interaction of the Palaeo-Tethys ocean – RETRACTION
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, p. 409
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation