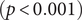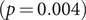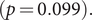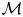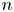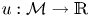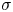303 results

Spectral and Spectral Element Methods for Fractional Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- September 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Macrolide-Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Several Regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Gender, Competition, and Performance: International Evidence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, pp. 1-63
-
- Article
- Export citation
Symbolic position analysis for three 6-DOF parallel mechanisms and new insight
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Epidemiology of tuberculosis among children in Beijing, China, 2012–2021
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, e44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of lncRNAKCNQ1OT1/miR-301b/Tcf7 axis in cardiac hypertrophy
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Autonomous predictive maintenance of quadrotor UAV with multi-actuator degradation
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
AMS 14C DATING AND STABLE ISOTOPE ANALYSIS ON AN 8-KYR OYSTER SHELL FROM TAIPEI BASIN: SEA LEVEL AND SST CHANGES
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quantifying stakeholders’ preference for implantable medical devices in China: a discrete choice experiment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Glucose Metabolism-Related Genes in the Progression from Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The algorithm and model of user data privacy protection psychological anxiety
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S114
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Adjoint-based high-order spectral method of wave simulation for coastal bathymetry reconstruction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2023, A41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mitigation of stimulated Raman scattering in a high-power fiber master oscillator power amplifier laser based on a dual-structure fiber grating
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, e92
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factors associated with depression among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2023, pp. 6424-6433
-
- Article
- Export citation
Zoonotic pathogens identified in rodents and shrews from four provinces, China, 2015–2022
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social mixing and network characteristics of COVID-19 patients before and after widespread interventions: A population-based study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE CHARGE-EXCHANGE CROSS-SECTIONS OF LOW-ENERGY CARBON IONS IN HELIUM AT GXNU
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessing Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perceptions of Medical Students Toward Emergency Preparedness and Disaster Medicine in Singapore
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2023, e438
-
- Article
- Export citation
A revisit to “On BMO and Carleson measures on Riemannian manifolds”
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
- Export citation
The articulatory properties of apical vowels in Hefei Mandarin
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Phonetic Association , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2023, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
- Export citation