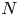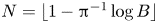2412 results
Clay Petrology Of Cambro-Ordovician Continental Margin, Cow Head Klippe, Western Newfoundland
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 25 / Issue 3 / June 1977
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2024, pp. 163-170
-
- Article
- Export citation
Starting vortices generated by an arbitrary solid body with any number of edges
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2024, A11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detection of and response to gender-based violence: a quality improvement project across three secondary mental health services in London
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Bulletin , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inertial coalescence of drops with some viscosity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, A77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
415 Intraoperative Molecular Imaging of Gliomas using Indocyanine-Conjugated Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Comparing MICADAS Gas Source, Direct Carbonate, and Standard Graphite 14C Determinations of Biogenic Carbonate
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 295-305
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Infrared Spectroscopic Analyses on the Nature of Water in Montmorillonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 42 / Issue 6 / December 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 702-716
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tropical vegetation productivity and atmospheric methane over the last 40,000 years from model simulations and stalagmites in Sulawesi, Indonesia
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 118 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, pp. 126-141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Subsurface scientific exploration of extraterrestrial environments (MINAR 5): analogue science, technology and education in the Boulby Mine, UK – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 23 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The genesis of metamorphosed Paleoproterozoic massive sulphide occurrences in central Colorado: geological, mineralogical and sulphur isotope constraints
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, pp. 1345-1375
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
DEVELOPMENT OF THE INTCAL DATABASE
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2023, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kilowatt-class high-energy frequency conversion to 95 J at 10 Hz at 515 nm
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2023, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Constantino de la Fuente (San Clemente, 1502–Seville, 1560). From acclaimed cathedral preacher to condemned ‘Lutheran’ heretic. By Frances Luttikhuizen. (Refo500 Academic Studies, 88.) Pp. 292. Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, 2022. €120. 978 3 525 56502 5
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History / Volume 74 / Issue 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2023, pp. 660-661
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Lumateperone (ITI-007) on Quality of Life and Functional Disability in the Treatment of Bipolar Depression
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, p. 238
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Lumateperone 42 mg in an Open-Label Switch Study in Patients with Stable Schizophrenia: Results by Previous Antipsychotic
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, pp. 235-236
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Lumateperone in Pooled Late-Phase Schizophrenia Trials: Number Needed to Treat, Number Needed to Harm, and Likelihood to Be Helped or Harmed
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, p. 243
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The motion of a layer of yield-stress material on an oscillating plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 959 / 25 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, A32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nontarget impacts of insecticide-based population control of eastern spruce budworm (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) on nontarget caterpillar communities and parasitism
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 155 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2023, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inertial and viscous dynamics of jump-to-contact between fluid drops under van der Waals attraction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 957 / 25 February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2023, A25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
User engagement with a popular food brand before, during and after a multi-day interactive marketing campaign on a popular live streaming platform
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2023, pp. 716-724
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation