272 results
Induced Thermoluminescence of some Clay Minerals
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / August 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 311-314
-
- Article
- Export citation
Head and Neck Cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines, Sixth Edition
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. S1-S224
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
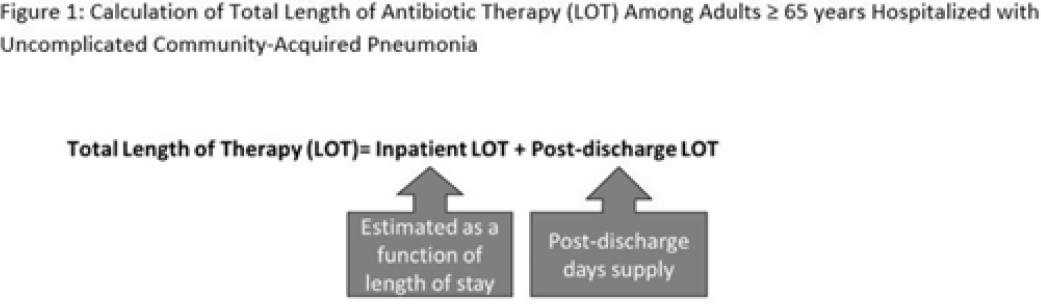
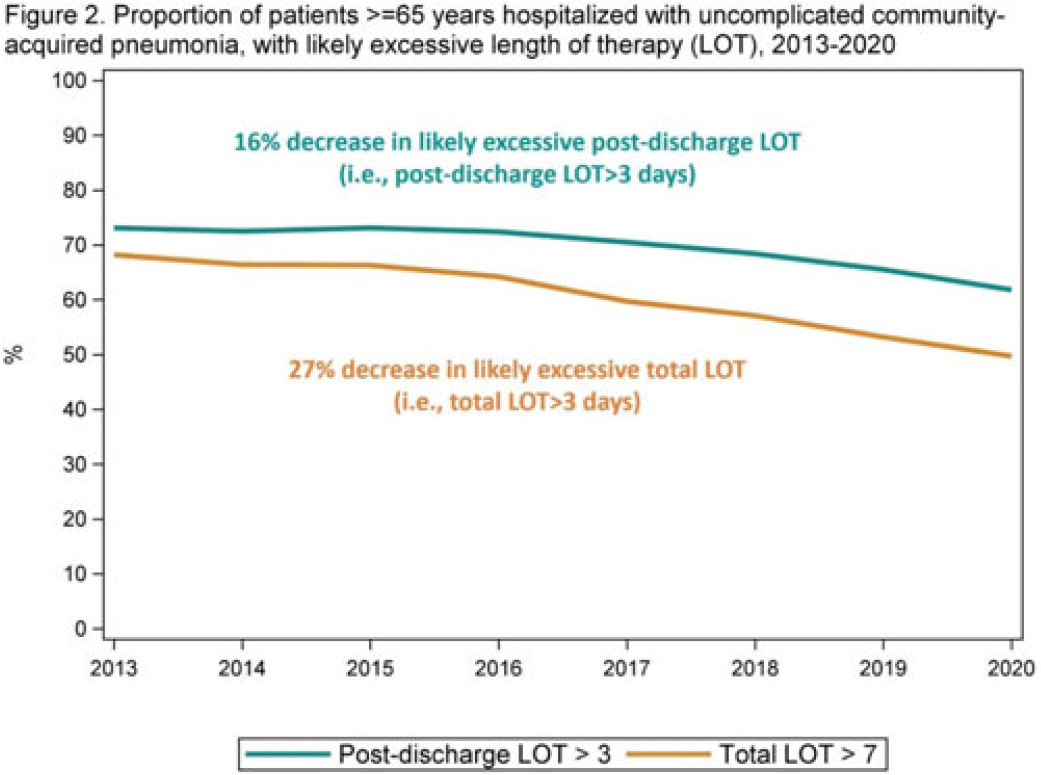
Length of antibiotic therapy among adults hospitalized with uncomplicated community-acquired pneumonia, 2013–2020
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, pp. 726-732
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Empowering the Participant Voice (EPV): Design and implementation of collaborative infrastructure to collect research participant experience feedback at scale
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2024, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The probiotic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus HN001 influences the architecture and gene expression of small intestine tissue in a piglet model
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, pp. 1289-1297
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

God and the Problems of Love
-
- Published online:
- 27 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2023
-
- Element
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Length of antibiotic therapy among adults aged ≥65 years hospitalized with uncomplicated community-acquired pneumonia, 2013-2020
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
338 The Alabama Genomic Health Initiative: Integrating Genomic Medicine into Primary Care
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 100-101
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Embedding community-engaged research principles in implementation science: The implementation science center for cancer control equity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2023, e82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nicolaus Mameranus: Poetry and Politics at the Court of Mary Tudor. By Matthew Tibble. Studies in Medieval and Reformation Traditions 220. Leiden and Boston: Brill, 2000. Xii + 389pp. €157 cloth.
-
- Journal:
- Church History / Volume 92 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2023, pp. 182-184
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) outbreaks in nursing homes involving residents who had completed a primary coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine series—13 US jurisdictions, July–November 2021
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2023, pp. 1005-1009
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Eilish Gregory. Catholics during the English Revolution, 1642–1660: Politics, Sequestration and Loyalty. Woodbridge: Boydell Press, 2021. Pp. 248. $115.00 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, pp. 240-241
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
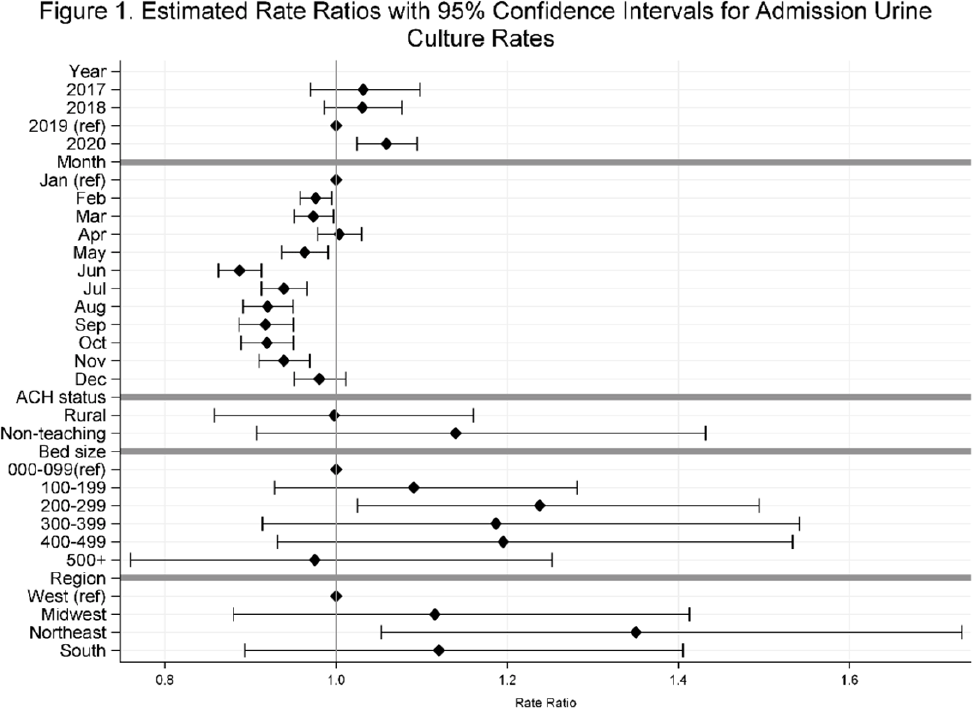
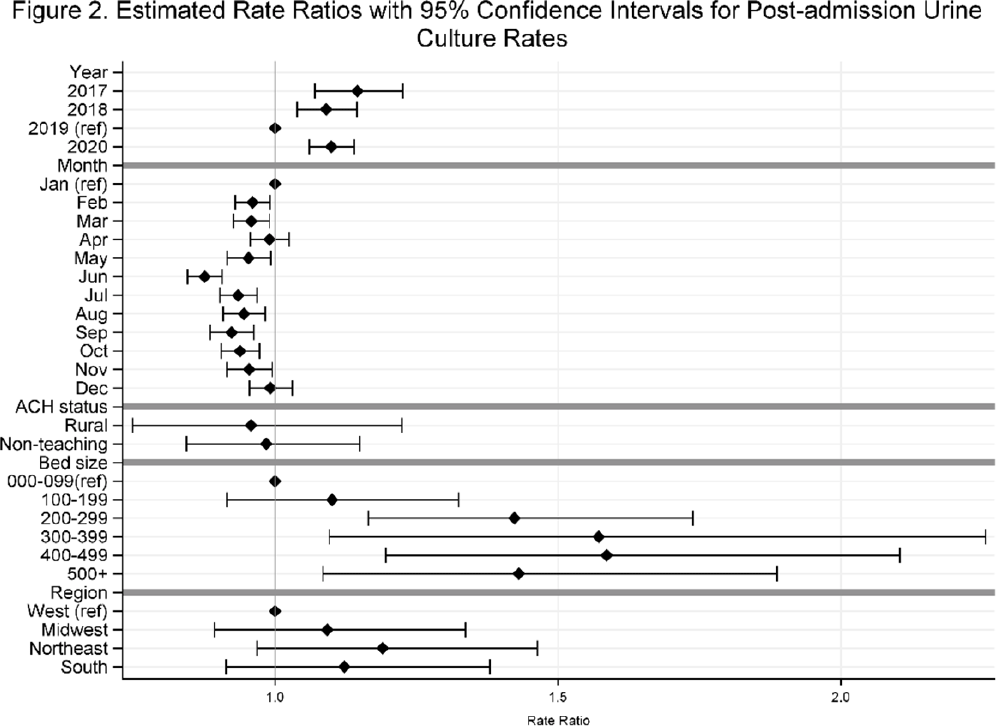
Temporal trends in urine-culture rates in the US acute-care hospitals, 2017–2020
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, p. s12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A New Radiocarbon Database for the Lower 48 States
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 87 / Issue 3 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, pp. 581-590
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Part 1 - Creating and Maintaining Identities
-
- Book:
- British and Irish Religious Orders in Europe, 1560-1800
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 07 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 21 January 2022, pp 19-20
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- British and Irish Religious Orders in Europe, 1560-1800
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 07 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 21 January 2022, pp i-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
List of Illustrations
-
- Book:
- British and Irish Religious Orders in Europe, 1560-1800
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 07 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 21 January 2022, pp vii-vii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Notes on Contributors
-
- Book:
- British and Irish Religious Orders in Europe, 1560-1800
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 07 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 21 January 2022, pp viii-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

British and Irish Religious Orders in Europe, 1560-1800
- Conventuals, Mendicants and Monastics in Motion
-
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 07 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 21 January 2022
Part 4 - Intellectual Movements
-
- Book:
- British and Irish Religious Orders in Europe, 1560-1800
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 07 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 21 January 2022, pp 201-202
-
- Chapter
- Export citation