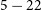806 results
Comparing parent-child interaction during wordless book reading, print book reading and imaginative play
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Child Language , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions among dental visits, 2019
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ageing as a Vegetarian and Vegan in the UK: Challenges and Barriers in Addressing their Dietary Preferences
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E333
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clay Minerals in Saprolite Overlying Hydrothermally Altered and Unaltered Rocks, Vera Epithermal Gold Deposit, Australia
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 6 / December 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 783-791
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey V: Cataloguing the sky at 1 367.5 MHz and the second data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, e003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Breeding allelopathy in cereal rye for weed suppression
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 72 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 30-40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Implementing a mentoring program for clinical research professionals: A novel professional development initiative for university health research staff
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, e247
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MWA rapid follow-up of gravitational wave transients: Prospects for detecting prompt radio counterparts
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2023, e050
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neuroticism as a moderator of symptom-related distress and depression in 4 noncancer end-of-life populations
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey III: Spectra and Polarisation In Cutouts of Extragalactic Sources (SPICE-RACS) first data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, e040
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review of extended coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) isolation duration among inpatients in a tertiary-care hospital—Iowa, 2020–2022
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, pp. 110-113
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Personality Change in a Trial of Psilocybin Therapy vs Escitalopram Treatment for Depression – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. 217
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An online experimental medicine trial on the effect of 28-day simvastatin administration on emotional processing, reward learning, working memory and salivary cortisol in healthy volunteers at risk for depression: OxSTEP protocol
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 June 2023, e110
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A scoping review of factors associated with antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter species infections in humans
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2023, e100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
D.1 Feasibility and impact of palliative care at any stage of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S53
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Personality change in a trial of psilocybin therapy v. escitalopram treatment for depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2023, pp. 178-192
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Body composition and motivations for accessing an innovative, digital community health engagement tool in socially deprived areas
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE3 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2023, E207
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Self-efficacy of participants in a holistic intervention to reduce unemployment and obesity in France and England
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE3 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2023, E220
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE SOPHIST'S PUZZLING EPISTÊMÊ IN THE SOPHIST
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly / Volume 73 / Issue 1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2023, pp. 53-65
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation