54 results
Implementing a continuous quality-improvement framework for tuberculosis infection prevention and control in healthcare facilities in China, 2017–2019
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 651-657
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Adsorption Behavior of Asphaltene on Clay Minerals and Quartz in a Heavy Oil Sandstone Reservoir with Thermal Damage
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 120-134
-
- Article
- Export citation
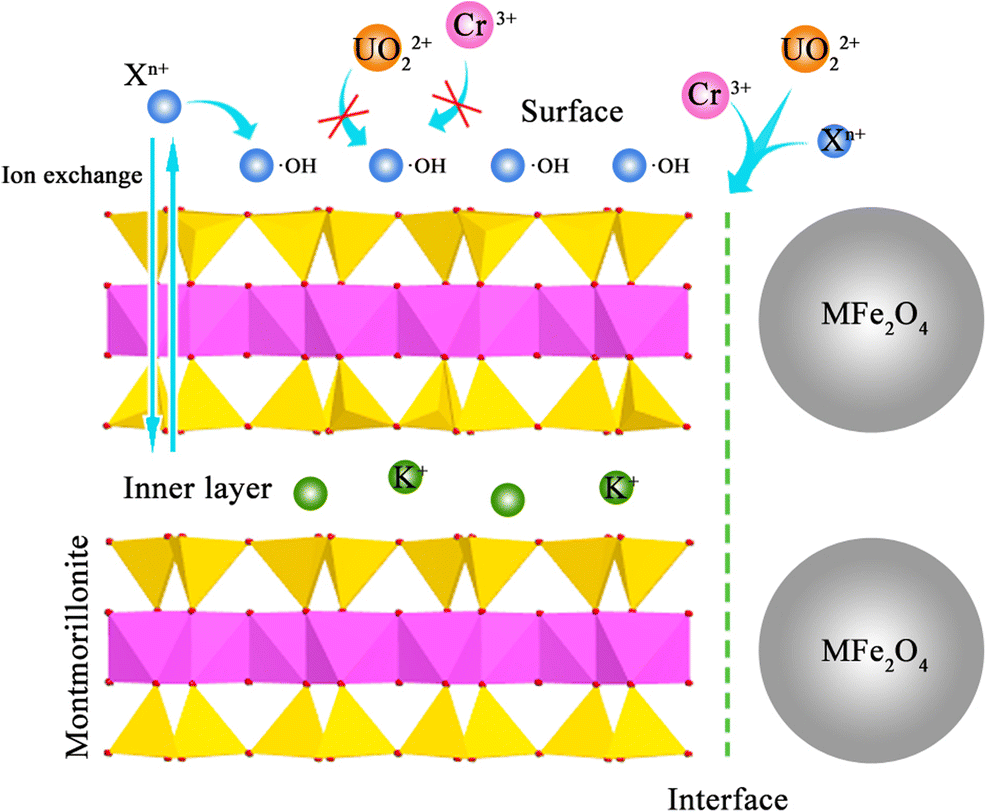
Competitive Adsorption of Uranyl and Toxic Trace Metal Ions at MFe2O4-montmorillonite (M = Mn, Fe, Zn, Co, or Ni) Interfaces
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 291-305
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ideological and political education in English courses of depression and anxiety students
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. S73-S74
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Lift generation mechanism of the leading-edge vortex for an unsteady plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dissociation between neuroanatomical and symptomatic subtypes in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stability and bifurcation of annular electro-thermo-convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 966 / 10 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2023, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Foraminifers and conodonts in the Danlu section, South China: implications for the Viséan–Serpukhovian boundary (Mississippian)
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, pp. 1131-1143
-
- Article
- Export citation
Quantitative evaluation of metamictisation of columbite-(Mn) from rare-element pegmatites using Raman spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 87 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, pp. 337-347
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Global linear instability analysis of thermal convective flow using the linearized lattice Boltzmann method
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 944 / 10 August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2022, A31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Salinity levels affect the lysine nutrient requirements and nutrient metabolism of juvenile genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2022, pp. 564-575
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of n-3 PUFA on left ventricular remodelling in chronic heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2022, pp. 1500-1509
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparison of ARIMA, ES, GRNN and ARIMA–GRNN hybrid models to forecast the second wave of COVID-19 in India and the United States
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2021, e240
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Glucosamine use, smoking and risk of incident chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a large prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 4 / 28 August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2021, pp. 721-732
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A prospective epidemiological analysis of controlling nutritional status score with the poor functional outcomes in Chinese patients with haemorrhagic stroke
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, pp. 192-199
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness, durability, and clinical correlates of the PEERS social skills intervention in young adults with autism spectrum disorder: the first evidence outside North America
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2021, pp. 966-976
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Successful Confinement of a Familial Cluster of COVID-19 in Qingdao, China, in the Early Phase of Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 December 2020, pp. 853-854
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Controlling Nutritional Status score is superior to Prognostic Nutritional Index score in predicting survival and complications in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a Chinese propensity score matching study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 11 / 14 December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2020, pp. 1190-1197
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation