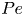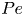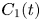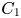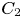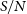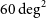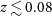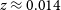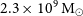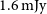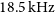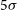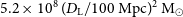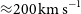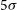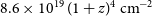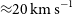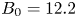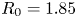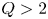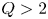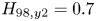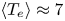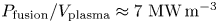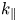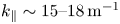317 results
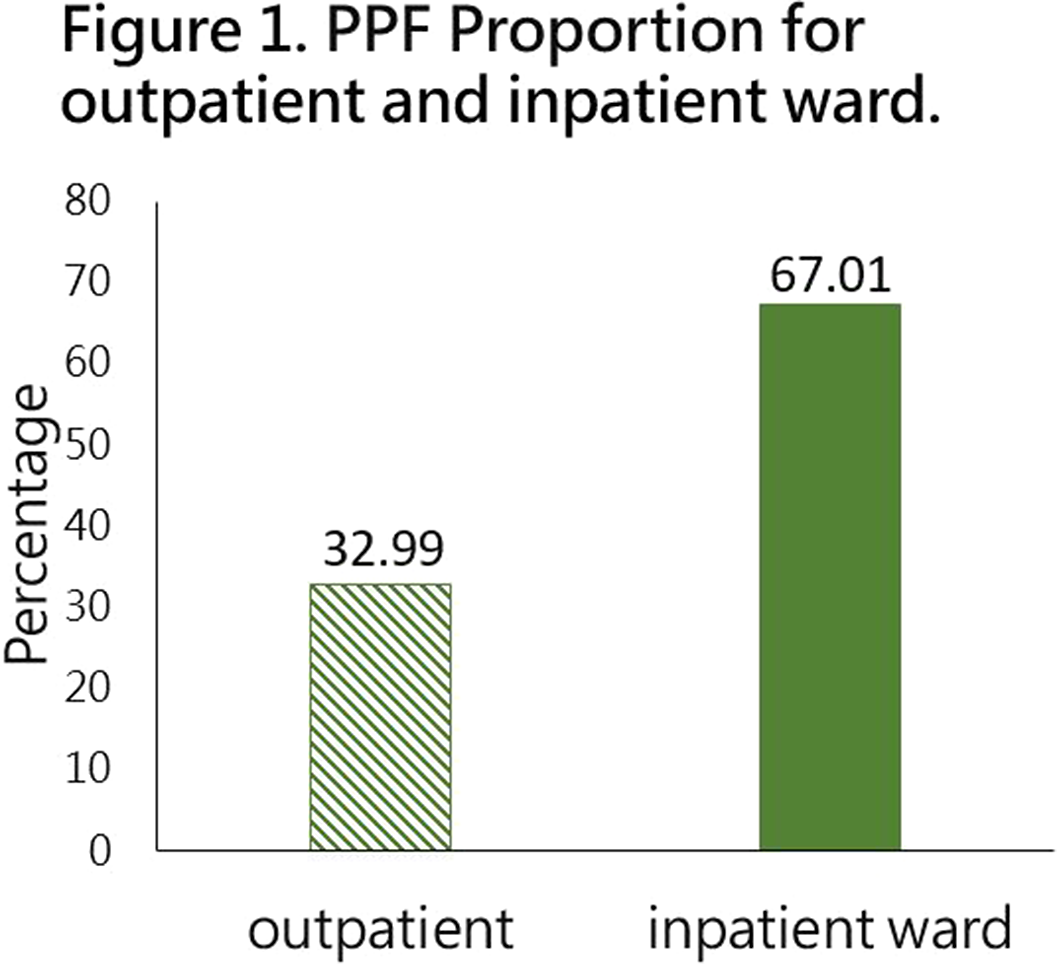
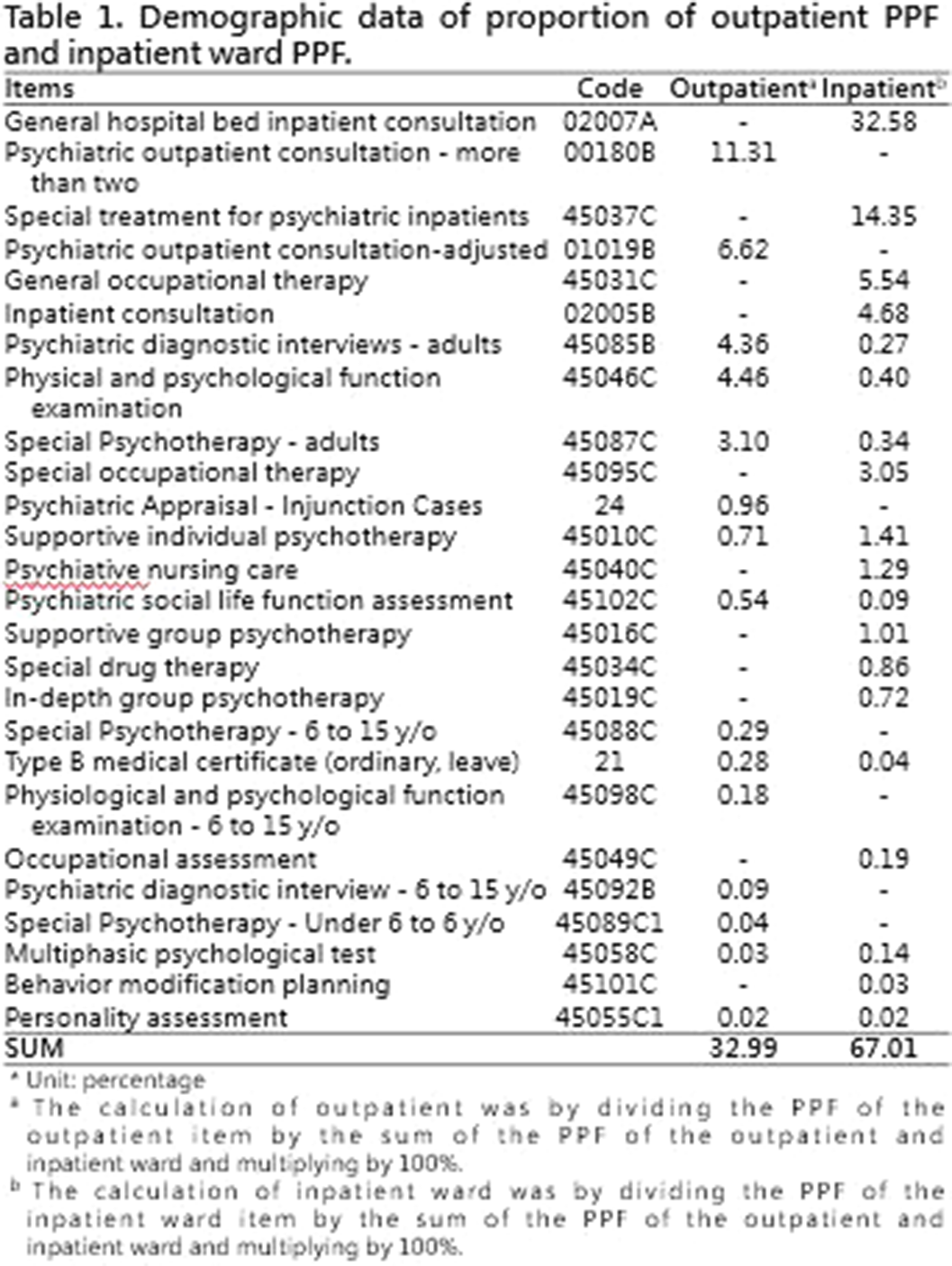
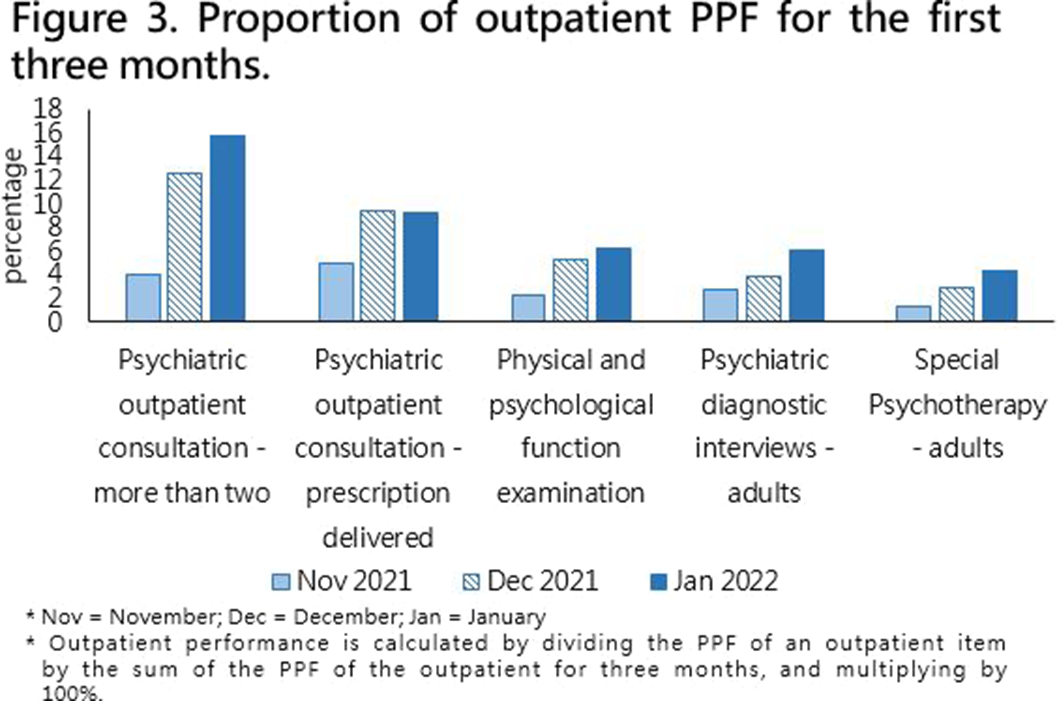
Taiwan National Health Insurance and the Difference between Proportional Physician Fee of Outpatient and Inpatient Ward in General Hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic : Case Report
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S310-S311
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A systematic review to assess the use of psilocybin in the treatment of headaches
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S617-S618
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Benzodiazepine Prescription for Anxiety Disorders Increase the Risk of Substance Use Disorders: A Retrospective Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S324
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
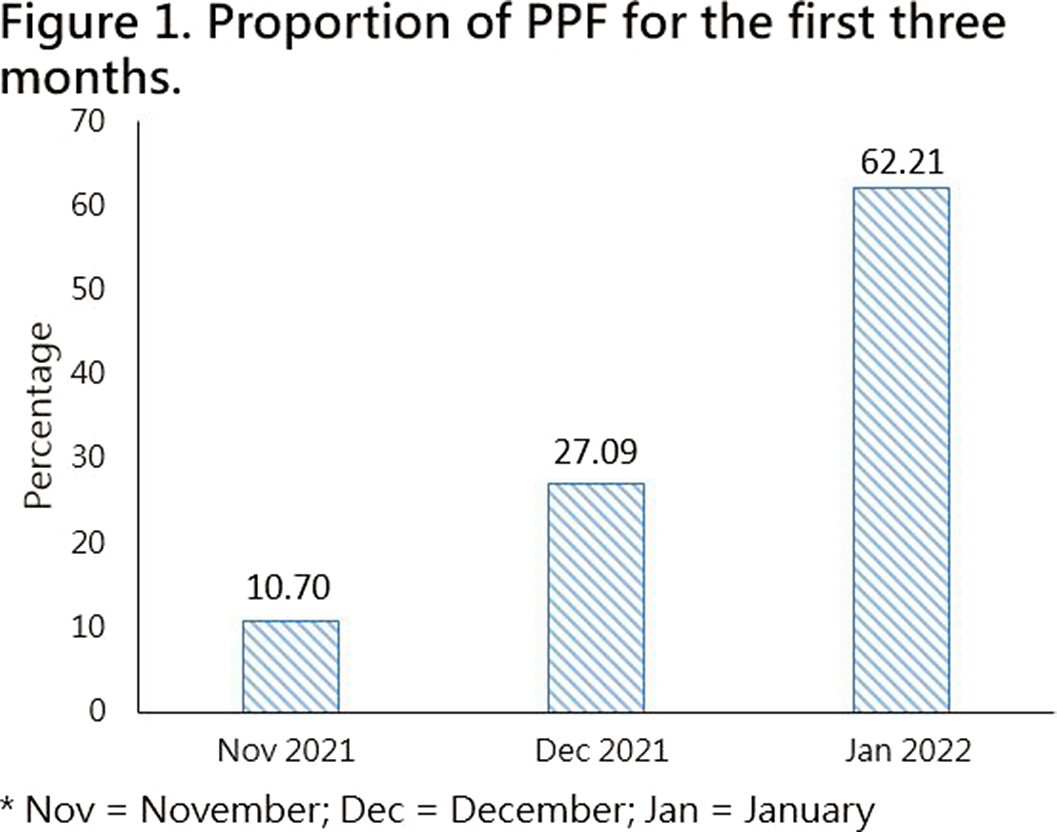
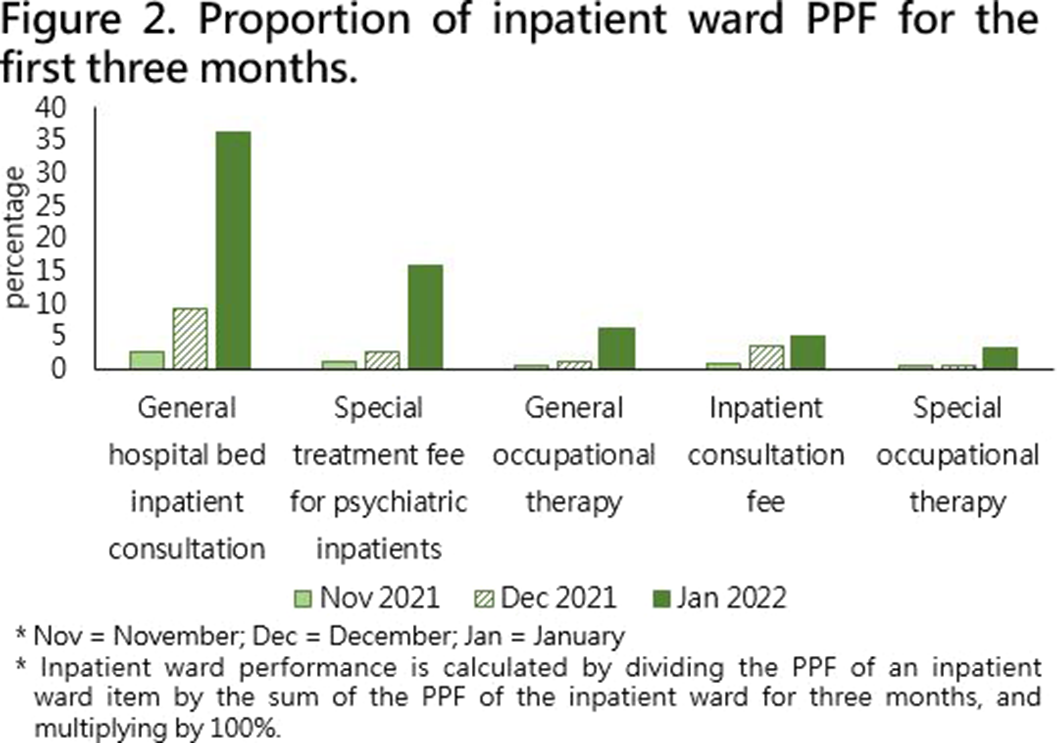
Taiwan National Health Insurance and Proportional Physician Fee of Psychiatrist in General Hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic : Case Report
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S1029-S1030
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A reduced model for a phoretic swimmer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 952 / 10 December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2022, A6
-
- Article
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Depression, anxiety and PTSD symptoms before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2022, pp. 5428-5441
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Derivation and validation of risk prediction for posttraumatic stress symptoms following trauma exposure
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 11 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2022, pp. 4952-4961
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ethical decision making in the 21st century: A useful framework for industrial-organizational psychologists
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 15 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2022, pp. 220-235
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular signalling involved in upper airway remodelling is enhanced in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, pp. 1096-1104
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mars: new insights and unresolved questions – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, p. 46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mars: new insights and unresolved questions
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 20 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 394-426
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Forager Mobility and Lithic Discard Probability Similarly Affect the Distance of Raw Material Discard from Source
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 86 / Issue 4 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, pp. 845-863
- Print publication:
- October 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Estimated number of N95 respirators needed for healthcare workers in acute-care hospitals during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 11 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2021, pp. 1318-1326
- Print publication:
- November 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Examining the independent and joint effects of genomic and exposomic liabilities for schizophrenia across the psychosis spectrum
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 29 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2020, e182
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A replication study of JTC bias, genetic liability for psychosis and delusional ideation
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 9 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, pp. 1777-1783
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Overview of the SPARC tokamak
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 86 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2020, 865860502
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Physics basis for the ICRF system of the SPARC tokamak
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 86 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2020, 865860506
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
4070 Association of Interpersonal Processes of Care and Health Outcomes in Patients with Type II Diabetes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue s1 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2020, pp. 80-81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation