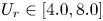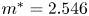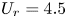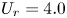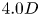790 results
3 - Fertility and Family Planning
-
-
- Book:
- India Population Report
- Published online:
- 15 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 27 June 2024, pp 46-109
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Statistical machine translation for Indic languages
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Processing ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Micro-perspective Analysis of the Demand for Greek and Non-Greek Yogurt in the United States Over Calendar Years 2018 to 2020
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics / Volume 56 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2024, pp. 329-351
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trilingual parallel processing: Do the dominant languages grab all the attention?
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mourning the Mother: Death and Feminine Authority in Odia Commemorations of Queen Victoria
-
- Journal:
- Victorian Literature and Culture / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / Spring 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 171-190
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Land Ownership Security, Farm Investment, and Investment Risk in Indian Agriculture: Evidence from Nationally Representative Survey
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics / Volume 56 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, pp. 278-296
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factors that promote the repulsion effect in preferential choice
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 19 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Three-dimensional transition of the flow past an elastically mounted circular cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stability analysis to identify improved lines of cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L. Taub.)
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2024, pp. 173-180
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factors affecting the dosimetry of high-dose rate intracavitary brachytherapy in cervical cancer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice / Volume 23 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic characterization of new source of resistance for tomato leaf curl New Delhi virus (ToLCNDV) from snapmelon (C. melo var. momordica)
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, pp. 78-86
-
- Article
- Export citation
Phenotypic profiling of lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) accessions enabled identification of promising lines for use in breeding for high yield, early flowering and desirable traits
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, pp. 69-77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Map of Fiji
-
- Book:
- Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024, pp xiii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024, pp vii-viii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Introduction: Reading the Fiji Hindi Demotic
-
- Book:
- Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024, pp 1-16
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
-
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024
Conclusion: Can the Subaltern Speak? Language Itself Speaks
-
- Book:
- Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024, pp 169-180
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Acknowledgements
-
- Book:
- Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024, pp ix-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - Introduction: Reading the Fiji Hindi Demotic
-
- Book:
- Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024, pp 17-42
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Select Bibliography
-
- Book:
- Subaltern Narratives in Fiji Hindi Literature
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 13 April 2024
- Print publication:
- 13 February 2024, pp 191-198
-
- Chapter
- Export citation