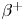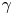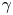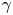42 results
A buffer-gas trap for the NEPOMUC positron beam: optimization studies with electrons
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, 935890602
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Annihilation-gamma-based diagnostic techniques for magnetically confined electron–positron pair plasma
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, 905890511
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Decentering European History from the Margins: Plural Visions of a Fragmented Modernity
-
- Journal:
- Annales. Histoire, Sciences Sociales: English Edition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2022, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Astrometric accuracy of snapshot fast radio burst localisations with ASKAP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2021, e050
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gaia EDR3 parallaxes of type I X-ray bursters and their implications on the models of type I X-ray bursts: A generic approach to the Gaia parallax zero point and its uncertainty
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2021, e048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comparison of Galactic electron density models using PyGEDM
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, e038
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A new frontier in laboratory physics: magnetized electron–positron plasmas
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 86 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2020, 155860601
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The transfer of land in medieval England from 1246 to 1430: the language of acquisition
-
- Journal:
- Continuity and Change / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2020, pp. 139-162
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Probing magnetar formation channels with high-precision astrometry: The progress of VLBA astrometry of the fastest-spinning magnetar Swift J1818.0–1607
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 16 / Issue S363 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2023, pp. 271-275
- Print publication:
- June 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
5 - To keep music alive
-
-
- Book:
- It's Basic Income
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 11 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2018, pp 36-38
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Follow Up of GW170817 and Its Electromagnetic Counterpart by Australian-Led Observing Programmes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 34 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2017, e069
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evolution of the low-frequency pulse profile of PSR B2217+47
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 13 / Issue S337 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2018, pp. 291-294
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Single Pulses from the Galactic Center Magnetar with the Very Large Array
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 13 / Issue S337 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2018, pp. 263-266
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Amenities and Rural Appalachia Economic Growth
-
- Journal:
- Agricultural and Resource Economics Review / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / April 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2016, pp. 107-132
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparing the Impacts of Retiree versus Working-Age Families on a Small Rural Region: An Application of the Wisconsin Economic Impact Modeling System
-
- Journal:
- Agricultural and Resource Economics Review / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / April 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2016, pp. 20-31
-
- Article
- Export citation

The Later Medieval Inquisitions Post Mortem
- Mapping the Medieval Countryside and Rural Society
-
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 26 May 2021
- Print publication:
- 21 July 2016
Contents
-
- Book:
- The Later Medieval Inquisitions <I>Post Mortem</I>
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 26 May 2021
- Print publication:
- 21 July 2016, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
9 - Proofs of Age 1246 to 1430: Their Nature, Veracity and Use as Sources
-
-
- Book:
- The Later Medieval Inquisitions <I>Post Mortem</I>
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 26 May 2021
- Print publication:
- 21 July 2016, pp 136-160
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- The Later Medieval Inquisitions <I>Post Mortem</I>
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 26 May 2021
- Print publication:
- 21 July 2016, pp i-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation