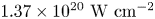57 results
Enhanced Proton Acceleration by Laser-Driven Collisionless Shock in the Near-Critical Density Target Embedding with Solid Nanolayers
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhancement of Magnetic Vortex Acceleration by Laser Interaction with Near-Critical Density Plasma inside a Hollow Conical Target
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Abnormalities in brain structure following childhood unpredictability: a mechanism underlying depressive and anxiety symptoms
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2023, pp. 299-307
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhanced proton acceleration from laser interaction with curved surface nanowire targets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2023, 905890113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Added sugar intake and its forms and sources in relation to risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: results from the Tianjin Chronic Low-grade Systemic Inflammation and Health cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 2094-2101
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rescue high-frequency oscillatory ventilation combined with intermittent mandatory ventilation for infants with acute respiratory distress syndrome after congenital heart surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 1165-1171
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary inflammatory index, inflammation biomarkers and preeclampsia risk: a hospital-based case–control study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2022, pp. 1528-1536
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protective effect of antioxidants on cardiac function in adult offspring exposed to prenatal overnutrition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 13 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2022, pp. 741-749
-
- Article
- Export citation
Organ meat consumption and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the Tianjin Chronic Low-grade Systemic Inflammation and Health cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 276-283
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficacy of cognitive therapy and behavior therapy for menopausal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2022, pp. 433-445
-
- Article
- Export citation
How Venture Capital Firms Choose Syndication Partners: The Moderating Effects of Institutional Uncertainty and Investment Preference
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 18 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2021, pp. 463-490
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between dietary patterns and risk of breast cancer in Chinese female population: a latent class analysis
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 15 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2020, pp. 4918-4928
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tectonic transition from subduction to retreat of the palaeo-Pacific plate: new geochemical constraints from the late Mesozoic volcanic sequence in eastern Fujian Province, SE China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 158 / Issue 6 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2020, pp. 1074-1108
-
- Article
- Export citation
Practice and exploration of 24-hour supervision model in personal protection supervision in a COVID-19 isolation ward
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 8 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2020, pp. 1027-1028
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anti-icing performance of hydrophobic material used for electromechanical drill applied in ice core drilling
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 66 / Issue 258 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 618-626
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of sugar-sweetened beverage intake with risk of metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents in urban China
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 23 / Issue 15 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2020, pp. 2770-2780
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anaemia, iron deficiency, iron-deficiency anaemia and their associations with obesity among schoolchildren in Guangzhou, China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 23 / Issue 10 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2020, pp. 1693-1702
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calculating individualized risk components using a mobile app-based risk calculator for clinical high risk of psychosis: findings from ShangHai At Risk for Psychosis (SHARP) program
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2019, pp. 653-660
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Burst behavior due to the quasimode excited by stimulated Brillouin scattering in high-intensity laser–plasma interactions
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2019, e58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Comprehensive Study of the 14C Source Term in the 10 MW High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 61 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2019, pp. 1169-1183
- Print publication:
- October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation