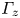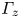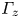189 results
Early Holocene exploitation of taro and yam among southern East Asian hunter-gatherers
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analysis and forecasting of syphilis trends in mainland China based on hybrid time series models
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2024, e93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The long-term spatio-temporal trends in burden and attributable risk factors of major depressive disorder at global, regional and national levels during 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for GBD 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Family-level moderators of daily associations between discrimination and distress among Mexican-origin youth
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Turbulent wake characteristics for a circular cylinder in proximity to a moving wall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 983 / 25 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Operational Dilemmas and Cadre Education and Training at a County Party School in China
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 258 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 513-528
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
International political relations on the anxiety disorders of Sino-Japanese Marine literature exchange
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
New sports rules combined with sertraline on Posttraumatic Stress of volleyball players
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S143
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Occurrence of metabolic syndrome in untreated bipolar disorders: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2023, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lift generation mechanism of the leading-edge vortex for an unsteady plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
A 24-year longitudinal study of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from patients with bacteraemia and urinary tract infections reveals the association between capsular serotypes, antibiotic resistance, and virulence gene distribution
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Choline-mediated hepatic lipid homoeostasis in yellow catfish: unravelling choline’s lipotropic and methyl donor functions and significance of ire-1α signalling pathway
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 202-213
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Book:
- Data Science for the Geosciences
- Published online:
- 25 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 17 August 2023, pp ix-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Data Science for the Geosciences
- Published online:
- 25 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 17 August 2023, pp 240-244
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

Data Science for the Geosciences
-
- Published online:
- 25 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 17 August 2023
-
- Textbook
- Export citation