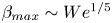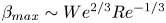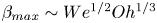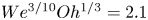62 results
Impacts of environmental factors on the aetiological diagnosis and disease severity of community-acquired pneumonia in China: a multicentre, hospital-based, observational study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, e80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Binary collision dynamics of equal-sized nanodroplets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2024, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prospect of ultrahigh-resolution fast neutron absorption spectroscopy based on a laser plasma electron accelerator
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factual and counterfactual learning in major adolescent depressive disorder, evidence from an instrumental learning study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2023, pp. 256-266
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of caregiver-mediated intervention: a pilot study for children with neurodevelopmental disorders
-
- Journal:
- Primary Health Care Research & Development / Volume 23 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2022, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comparison between three-dimensional, transient, thermomechanically coupled first-order and Stokes ice flow models
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 69 / Issue 275 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2022, pp. 513-524
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Efficacy and acceptability of second-generation antipsychotics with antidepressants in unipolar depression augmentation: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 12 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2022, pp. 2224-2231
-
- Article
- Export citation
Scaling laws of the maximum spreading factor for impact of nanodroplets on solid surfaces
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 937 / 25 April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2022, A12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Risk factors for sporadic listeriosis in Beijing, China: a matched case–control study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2022, e62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Correlations among spiritual care competence, spiritual care perceptions and spiritual health of Chinese nurses: A cross-sectional correlational study
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2022, pp. 243-254
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sex influences the association between appendicular skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 June 2021, pp. 1613-1620
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late-life sleep duration associated with amnestic mild cognitive impairment
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2021, pp. 439-448
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparative efficacy of pharmacological treatments on measures of self-rated functional outcomes using the Sheehan Disability Scale in patients with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2021, pp. 428-436
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dissociation of Proactive and Reactive Cognitive Control in Individuals with Schizotypy: An Event-Related Potential Study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 27 / Issue 10 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2021, pp. 981-991
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detection of polymorphic simple-sequence repeat markers that show linkage to a novel sugarcane brown rust disease resistance gene in resistant and susceptible genetic pools
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 18 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2020, pp. 397-403
-
- Article
- Export citation
Associations between dietary patterns and physical fitness among Chinese elderly
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 14 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2020, pp. 4466-4473
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Monolayer Graphene-covered Grids Enable 2.6-Å Single-particle Cryo-EM Reconstruction of 52-kDa Streptavidin
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2020, pp. 1030-1031
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effectiveness of mirtazapine as add-on to paroxetine v. paroxetine or mirtazapine monotherapy in patients with major depressive disorder with early non-response to paroxetine: a two-phase, multicentre, randomized, double-blind clinical trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 7 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2020, pp. 1166-1174
-
- Article
- Export citation
NiSx@MoS2 heterostructure prepared by atomic layer deposition as high-performance hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalysts in alkaline media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 7 / 14 April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2019, pp. 822-830
- Print publication:
- 14 April 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic analysis of sugarcane brown rust resistance genes in wild sugarcane germplasm Erianthus rockii ‘Yundian 95-19’ and Erianthus rockii ‘Yundian 95-20’
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 17 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2019, pp. 460-463
-
- Article
- Export citation