48 results
Effective aero-optical suppression by steady wall blowing and wall suction schemes for supersonic turbulent boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1312 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 1037-1047
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of sheared E × B flow on the blob dynamics in the scrape-off layer of HL-2A tokamak
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2022, 905880605
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Patients’ Attitude to Breast Conserving Surgery for Breast Cancer in West China
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / January 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, 24-E820
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Self-management Patterns in Chinese People with Schizophrenia – Cluster Analysis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 30 / Issue S1 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of goldfish (Carassius auratus) population size and body condition on the transmission of Gyrodactylus kobayashii (Monogenea)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 144 / Issue 9 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2017, pp. 1221-1228
-
- Article
- Export citation
Altered corticostriatal functional connectivity in individuals with high social anhedonia
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / January 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2015, pp. 125-135
-
- Article
- Export citation
Estimating nutrient requirements for winter oilseed rape based on QUEFTS analysis
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 154 / Issue 3 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2015, pp. 425-437
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genotype differences in photosynthetic characteristics and nitrogen efficiency of new-type oilseed rape responding to low nitrogen stress
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 153 / Issue 6 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2014, pp. 1030-1043
-
- Article
- Export citation
Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection in Bai and Han ethnic groups in southwestern China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 143 / Issue 4 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2014, pp. 881-886
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neural correlates of the abolished self-referential memory effect in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 44 / Issue 3 / February 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2013, pp. 477-487
-
- Article
- Export citation
Arctic and Antarctic four-month oscillations detected from Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit-A measurements
-
- Journal:
- Antarctic Science / Volume 24 / Issue 5 / 13 September 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2012, pp. 507-513
-
- Article
- Export citation
EXISTENCE OF INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS FOR SUBLINEAR ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / September 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2012, pp. 535-545
- Print publication:
- September 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Epidemiological and molecular analysis of a waterborne outbreak of norovirus GII.4
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 140 / Issue 12 / December 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2012, pp. 2282-2289
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cool and hot executive functions in medication-naive attention deficit hyperactivity disorder children
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 41 / Issue 12 / December 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2011, pp. 2593-2602
-
- Article
- Export citation
3D Structure Determination from HRTEM and Electron Diffraction Tomography
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 15 / Issue S2 / July 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2009, pp. 56-57
- Print publication:
- July 2009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation



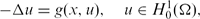
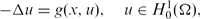 for all
for all 