707 results
Mixed infections with Opisthorchis viverrini and intestinal flukes in residents of Vientiane Municipality and Saravane Province in Laos
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 79 / Issue 3 / September 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 283-289
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimization of nonlinear turbulence in stellarators
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, 905900210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Effect of Microbial Fe(III) Reduction on Smectite Flocculation
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / December 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 572-579
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterization of Microbially Fe(III)-Reduced Nontronite: Environmental Cell-Transmission Electron Microscopy Study
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / August 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 382-389
-
- Article
- Export citation
24 Associations Between Positive Psychological Factors and Neurocognitive Functioning in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 337
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Conceptualization, development, and early dissemination of eMPACTTM: A competency-based career navigation system for translational research professionals
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
United we thrive: friendship and subsequent physical, behavioural and psychosocial health in older adults (an outcome-wide longitudinal approach)
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2023, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Treatment of hypoplastic left heart syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2023, pp. 659-666
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessing possible moderators on the association between frequency of contact with non-cohabitating adult children and depressive symptoms among community-dwelling older adults
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S222
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Validation of a Brief Internet-based Self-report Measure of Maladaptive Personality and Interpersonal Schema
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S527
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Amisulpride Augmentation in Schizophrenia Patients with Poor Response to Olanzapine: A 4-week, Randomized, Rater-Blind, Controlled, Pilot Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1093
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
VIRTUALLY HOSTED HACKATHONS FOR DESIGN RESEARCH: LESSONS LEARNED FROM THE INTERNATIONAL DESIGN ENGINEERING ANNUAL (IDEA) CHALLENGE 2022
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, pp. 3811-3820
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The influence of subsurface architecture on scour hole formation in the Rhine–Meuse delta, the Netherlands
-
- Journal:
- Netherlands Journal of Geosciences / Volume 102 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of sedentary behavior and emotional support on prenatal psychological distress and birth outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, pp. 6792-6805
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between obsessive-compulsive disorder and the risk of schizophrenia using the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort: a retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Potential overestimation of cognitive impairment because of hearing loss: impact of test modalities on cognitive test scores
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2023, pp. 845-850
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of the Correlation between Gaze Avoidance and Schizophrenia Psychopathology with Deep Learning-based Emotional Recognition
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S315
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
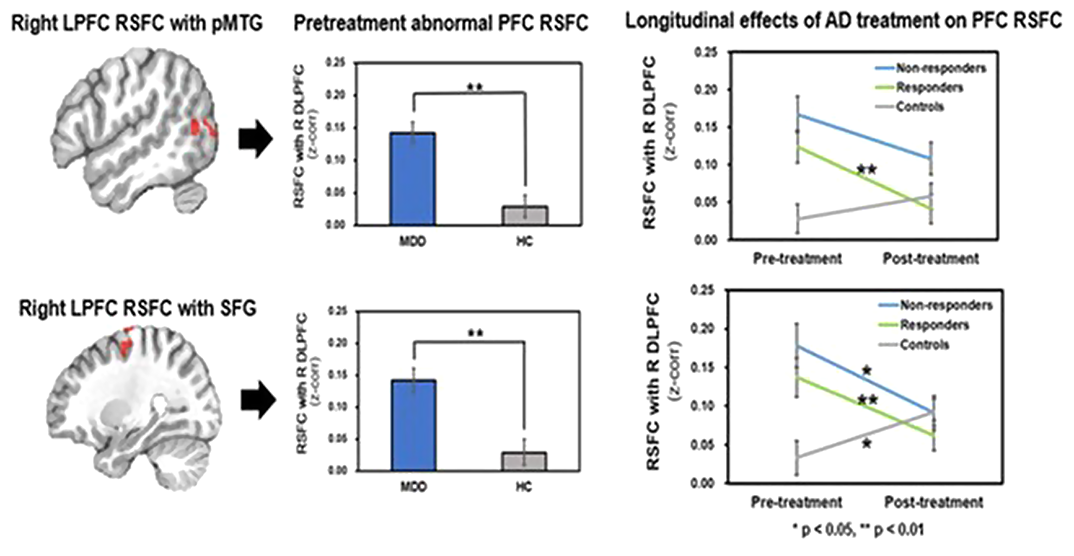
Longitudinal effects of antidepressant treatment on resting state functional connectivity in adolescents with major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A qualitative study on the symptoms and psychological characteristics of young Hwa-Byung patients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S546
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation