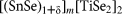96 results
Highly pathogenic avian influenza causes mass mortality in Sandwich Tern Thalasseus sandvicensis breeding colonies across north-western Europe
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 34 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Particle tracking in snow avalanches with in situ calibrated inertial measurement units
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
8 - Planning and the environment in England, 2010–22: cutting ‘green crap’, Brexit and environmental crises
-
-
- Book:
- Planning in a Failing State
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 27 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 23 November 2023, pp 120-137
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Particle trajectories, velocities, accelerations and rotation rates in snow avalanches
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perceptions of regional origin and social attributes of phonetic variants used in Iberian Spanish
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Linguistic Geography / Volume 11 / Issue 2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 119-143
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 9 - Genetic Causes of Medication-Resistant Epilepsy
-
-
- Book:
- Medication-Resistant Epilepsy
- Published online:
- 20 August 2020
- Print publication:
- 10 September 2020, pp 69-78
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Equivalency of the diagnostic accuracy of the PHQ-8 and PHQ-9: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 16 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2019, p. 2816
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Equivalency of the diagnostic accuracy of the PHQ-8 and PHQ-9: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 8 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2019, pp. 1368-1380
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electronic structure of designed [(SnSe)1+δ]m[TiSe2]2 heterostructure thin films with tunable layering sequence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2019, pp. 1965-1975
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Competitive interplay of deposition and etching processes in atomic layer growth of cobalt and nickel metal films
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 33 / Issue 24 / 28 December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2018, pp. 4241-4250
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Probability of major depression diagnostic classification using semi-structured versus fully structured diagnostic interviews
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 212 / Issue 6 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2018, pp. 377-385
- Print publication:
- June 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The State of Matter in Simulations of Core-Collapse supernovae—Reflections and Recent Developments
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 34 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2017, e067
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Computational fluid dynamic (CFD) simulation of snowdrift in alpine environments, including a local weather model, for operational avalanche warning
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 48 / 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2017, pp. 150-158
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Elucidating changes in the degree of tracer dispersion in a subglacial channel
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 37 / 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2017, pp. 275-280
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
115 year ice-core data from Akademii Nauk ice cap, Severnaya Zemlya: high-resolution record of Eurasian Arctic climate change
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 55 / Issue 189 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2017, pp. 21-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multivariate parameter optimization for computational snow avalanche simulation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 61 / Issue 229 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2017, pp. 875-888
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A facilitated approach to family case conferencing for people with advanced dementia living in nursing homes: perceptions of palliative care planning coordinators and other health professionals in the IDEAL study
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 29 / Issue 10 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2017, pp. 1713-1722
-
- Article
- Export citation
Determination of a Cutoff Time Point for Prophylactic Exchange of Central Venous Catheters for Prevention of Central Venous Catheter–Related Bloodstream Infections in Patients with Hematological Malignancies
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 38 / Issue 7 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2017, pp. 888-889
- Print publication:
- July 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) interference with corn across the northcentral United States
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 52 / Issue 6 / December 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 1034-1038
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biased Low Incidence of Central Venous Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections in Controlled Clinical Trials?
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 37 / Issue 5 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2016, pp. 617-619
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation