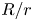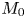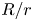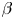308 results
Investigation of free surface effect on the cavity expansion and contraction in high-speed water entry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2024, A53
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shared and distinct electroencephalogram microstate abnormalities across schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Trauma diagnostic-related target proteins and their detection techniques
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The protective effect of vitamin D supplementation as adjunctive therapy to antidepressants on brain structural and functional connectivity of patients with major depressive disorder: a randomized controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sequence variations in GATA4 and CITED2 gene among patients with cardiac septation defects from Xinjiang, China
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Temporal changes in brain morphology related to inflammation and schizophrenia: an omnigenic Mendelian randomization study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Models of mild cognitive deficits in risk assessment in early psychosis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Release of Mg and Fe From the Octahedral Sheets During the Transformation of Montmorillonite Into Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 453-462
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural bioinformatics studies of six human ABC transporters and their AlphaFold2-predicted water-soluble QTY variants
-
- Journal:
- QRB Discovery / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 January 2024, e1
- Print publication:
- 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Correlation between Photoluminescence Properties of Surface Defects and Laser-Induced Damage Threshold of Fused Silica
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dynamic structure–function coupling across three major psychiatric disorders
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 8 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2023, pp. 1629-1640
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary inclusion of Clostridium butyricum cultures alleviated impacts of high-carbohydrate diets in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides)
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1308-1325
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between pro-inflammatory diet and liver cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, pp. 2780-2789
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mach reflection of three-dimensional curved shock waves on V-shaped blunt leading edges
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2023, A45
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mismatch analysis of all-fiber coherent beam combiners based on the self-imaging effect
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary chenodeoxycholic acid attenuates high-fat diet-induced growth retardation, lipid accumulation and bile acid metabolism disorder in the liver of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 921-934
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
SPECIFICATION TESTS FOR TIME-VARYING COEFFICIENT PANEL DATA MODELS – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2023, p. 1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of monolaurin on intestinal barrier, blood biochemical profile, immunity and antioxidant function in porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus-infected piglets
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2023, pp. 185-192
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation