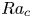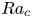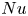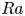32 results
Association between cortical thickness or surface area and divergent thinking in patients with bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Heat transport and flow structure in thermal convection with two liquid layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risks and familial coaggregation of death by suicide, accidental death and major psychiatric disorders in first-degree relatives of individuals who died by suicide
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2023, pp. 465-470
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Appetite hormone dysregulation, body mass index, and emotional dysregulation in nonobese adolescents with first-episode schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a cross-sectional association study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, pp. 629-636
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risk of parental psychiatric disorders among adolescents with major depressive disorder according to response to antidepressant treatment: does the type of antidepressant matter?
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2023, pp. 614-619
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluating the performance of machine learning models for automatic diagnosis of patients with schizophrenia based on a single site dataset of 440 participants
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2021, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Global cognitive dysfunction and β-amyloid neuropathology in late-life and treatment-resistant major depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 16 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2021, pp. 4116-4126
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inflammation, cognitive dysfunction, and suicidal ideation among patients with major depression
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 27 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2021, pp. 724-730
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of common neural substrates with connectomic abnormalities in four major psychiatric disorders: A connectome-wide association study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2020, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cardiometabolic disease risk among siblings of patients with major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 12 / Issue 3 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2020, pp. 530-535
-
- Article
- Export citation
Familial coaggregation of major psychiatric disorders in first-degree relatives of individuals with autism spectrum disorder: a nationwide population-based study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 8 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2020, pp. 1437-1447
-
- Article
- Export citation
Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over cerium–tungsten–titanium mixed oxide catalyst: Synergistic promotional effect of H2O2 and Ce4+
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2020, pp. 2218-2229
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Role of obesity in systemic low-grade inflammation and cognitive function in patients with bipolar I disorder or major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 26 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2020, pp. 521-527
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficacy of low-dose ketamine infusion in anxious vs nonanxious depression: revisiting the Adjunctive Ketamine Study of Taiwanese Patients with Treatment-Resistant Depression
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2020, pp. 362-367
-
- Article
- Export citation
Profile of Chest Injuries and Oxygen Therapy in Trauma Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure after the Jiangsu Tornado in China: A Retrospective Study
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, pp. 335-340
- Print publication:
- June 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Familial coaggregation of major psychiatric disorders among first-degree relatives of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a nationwide study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2020, pp. 680-687
-
- Article
- Export citation
Increased risk of type 2 diabetes among the siblings of patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2019, pp. 453-459
-
- Article
- Export citation
Risk and coaggregation of major psychiatric disorders among first-degree relatives of patients with bipolar disorder: a nationwide population-based study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 49 / Issue 14 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2018, pp. 2397-2404
-
- Article
- Export citation
Risk of suicide attempts in adolescents and young adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a nationwide longitudinal study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 212 / Issue 4 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2018, pp. 234-238
- Print publication:
- April 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation