296 results
Proton acceleration from optically tailored high-density gas jet targets
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, 965900201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular identification of Anisakis species from Pleuronectiformes off the Portuguese coast
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 80 / Issue 1 / March 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 47-51
-
- Article
- Export citation
FC23: Dementia and Triadic (Doctor-Patient-Carer) Interactions in Primary Care
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 84-85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P123: Cognitive Disorders and Impact on Caregivers: The COGCARE Study protocol
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 252-253
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Upper Cretaceous Clayey Levels from Western Portugal (Aveiro and Taveiro Regions): Clay Mineral and Trace-Element Distribution
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 3 / June 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 315-327
-
- Article
- Export citation
Proton and helium ions acceleration in near-critical density gas targets by short-pulse Ti:Sa PW-class laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2023, 965890601
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Leucocytozoon cariamae n. sp. and Haemoproteus pulcher coinfection in Cariama cristata (Aves: Cariamiformes): first mitochondrial genome analysis and morphological description of a leucocytozoid in Brazil
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 150 / Issue 14 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2023, pp. 1296-1306
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Capgras Syndrome as a Manifestation of a Neurodegenerative Disease – What do we know?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S359
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Portuguese version of the Screen for Disordered Eating: Validity and reliability in middle aged and older women
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S424-S425
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder: A Diagnostic Challenge
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S701
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A Psychosis Superspectrum in Borderline Personality Disorder?
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S177
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Capgras syndrome conceptualization: from a delusional disorder to a structural neurological phenomenon
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1073
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Serotonin reuptake inhibitors and its cognitive burden…or relief.: A brief review
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Development and first validation of the Portuguese version of the Big Three Perfectionism Scale–Short Form (BTPS-SF)
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S174-S175
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
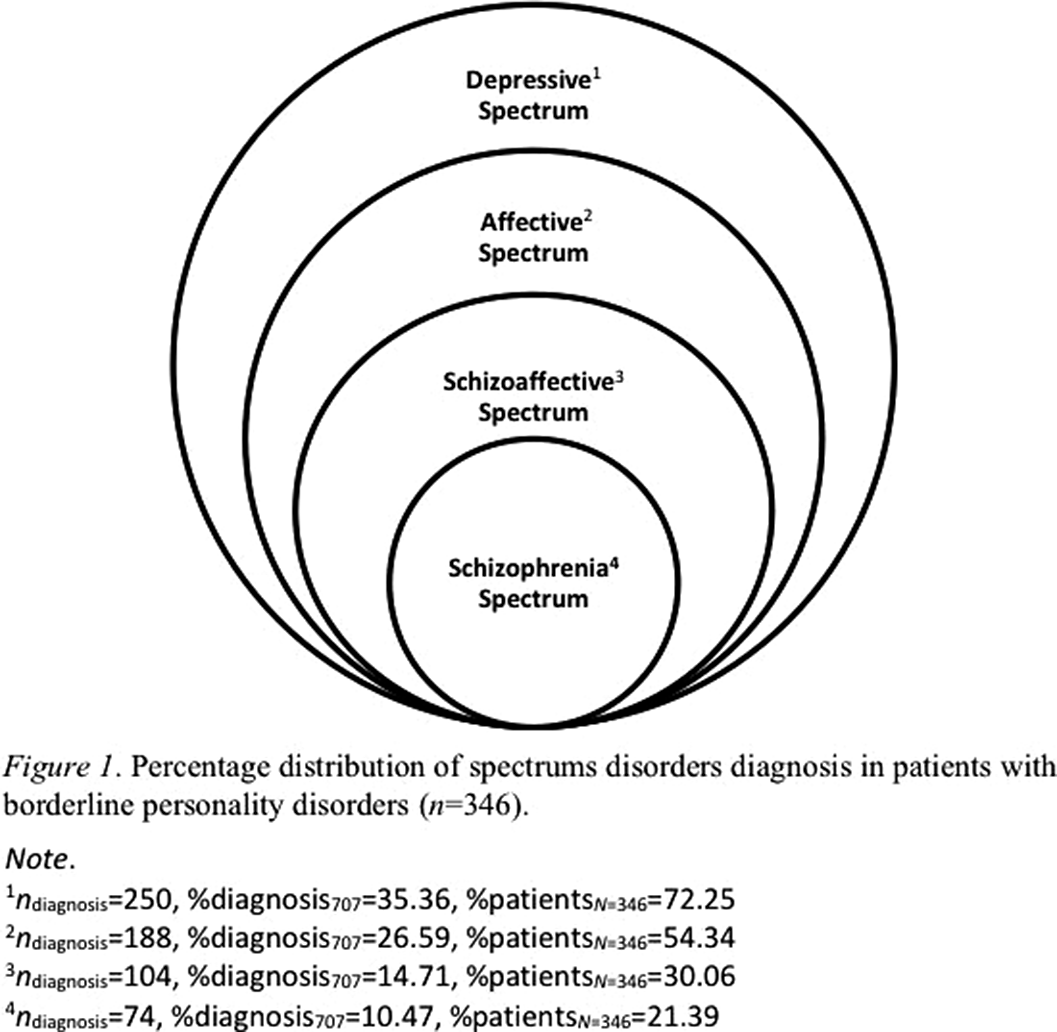
Diagnostic stability of 346 patients with borderline personality disorder based on retrospective clinical records
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S625-S626
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Hormonal and behavioural stress responses to capture and radio-collar fitting in free-ranging pampas deer (Ozotoceros bezoarticus)
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / November 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 437-446
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effects of powerlines on bustards: how best to mitigate, how best to monitor? – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 October 2022, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effects of powerlines on bustards: how best to mitigate, how best to monitor?
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2022, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Further Validation of the Short Form of the Self-Compassion Scale in a sample of Portuguese Medicine Students
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S178
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Reinforcing the new diagnosis of Complex Post-Traumatic Stress disorder (CPTSD) of ICD-11: exploring the clinical outcomes in youth exposed to complex trauma
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. S448-S449
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation