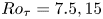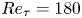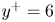64 results
Effects of streamwise rotation on helicity and vortex in channel turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, A50
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dietary inflammatory potential is associated with higher odds of hepatic steatosis in US adults: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 2936-2944
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multiscale dynamics in streamwise-rotating channel turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, A14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genetic and Environmental Influences on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids Across Age-Groups
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 223-230
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morph-specific fitness throughout the life cycle of the grain aphid, nonhost-alternating, holocyclic Sitobion avenae (Hemiptera: Aphididae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, pp. 658-664
-
- Article
- Export citation
Laser chirp controlled relativistic few-cycle mid-infrared pulse generation
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2023, e57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of patients with SARS-COV-2 PCR re-positivity after recovering from COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Healthy and unhealthy low-carbohydrate diets and plasma markers of cardiometabolic risk
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2022, pp. 137-146
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quasi-dynamic subgrid-scale kinetic energy equation model for large-eddy simulation of compressible flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 947 / 25 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2022, A22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transfers of energy and helicity in helical rotating turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, A19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tracking Degradation in Individual Catalyst Nanoparticles Under Fuel Cell-Relevant Cycling Conditions by Identical-Location STEM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2614-2617
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
TNF-α/anti-TNF-α drugs and its effect on pregnancy outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 24 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2022, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Helicity distributions and transfer in turbulent channel flows with streamwise rotation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 940 / 10 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2022, A18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Diets with higher insulinaemic potential are associated with increased risk of overall and cardiovascular disease-specific mortality
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2021, pp. 2011-2020
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Schistosomiasis in the People's Republic of China – down but not out
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 149 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, pp. 218-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal trajectory analysis of antipsychotic response in patients with schizophrenia: 6-week, randomised, open-label, multicentre clinical trial – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 5 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2021, e153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of dietary inflammatory potential with risk of overall and cause-specific mortality
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2021, pp. 1878-1887
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of the pre-pregnancy weight status with anaemia and the erythropoiesis-related micronutrient status
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 18 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 June 2021, pp. 6247-6257
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation