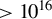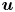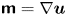284 results
Longitudinal Beam Dynamics for the Heavy-Ion Synchrotron Booster Ring at HIAF
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effective aero-optical suppression by steady wall blowing and wall suction schemes for supersonic turbulent boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1312 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 1037-1047
-
- Article
- Export citation
Low-order moments of the velocity gradient in homogeneous compressible turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 947 / 25 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2022, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring the Validity Limits of Direct Ptychographic Methods to Analyse 4D Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy Datasets
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 420-421
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Study on the monitoring and classification of winter wheat freezing injury in spring based on 3S technology
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 159 / Issue 9-10 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2022, pp. 623-635
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stable transport of relativistic electron beams in plasmas
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2022, 905880105
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seasonality of suicide: a multi-country multi-community observational study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 29 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, e163
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mathematical model describing CoViD-19 in São Paulo, Brazil – evaluating isolation as control mechanism and forecasting epidemiological scenarios of release
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2020, e155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Substituting chemical fertilizer nitrogen with organic manure and comparing their nitrogen use efficiency and winter wheat yield
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 158 / Issue 4 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2020, pp. 262-268
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 5 - Pharmacogenomics and Psychopharmacology
- from Part 1 - Basic Science and General Principles
-
-
- Book:
- Seminars in Clinical Psychopharmacology
- Published online:
- 29 May 2020
- Print publication:
- 18 June 2020, pp 151-202
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Long-term safety of long-acting risperidone microspheres
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 17 / Issue S1 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 193s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prevalence of depressive disorders in shanghai children aged 8∼12 years
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / March 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 623
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The relationship of family characteristics and bipolar disorder using causal-pie models
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / January 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 36-43
-
- Article
- Export citation
1175 – The Effect Of Mk-801 On The Erk-creb Signal System In Prenatally Stressed Offspring Rats
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E549
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Plasma-based proteomics reveals lipid metabolic and immunoregulatory dysregulation in post-stroke depression
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / June 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 307-315
-
- Article
- Export citation
Role of DRD2 and ALDH2 genes in bipolar II disorder with and without comorbid anxiety disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / March 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 142-148
-
- Article
- Export citation