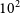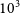194 results
Hydrogen Positions in Dickite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 32 / Issue 6 / December 1984
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 483-485
-
- Article
- Export citation
Head and Neck Cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines, Sixth Edition
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. S1-S224
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Community scientist program provides bi-directional communication and co-learning between researchers and community members
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
42 Real-time Associations Among MS Symptoms and Cognitive Dysfunction Using Ecological Momentary Assessment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 555-556
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Barriers to Surgical Intervention and Factors Influencing Motor Outcomes in Patients with Severe Peripheral Nerve Injury: A Province Wide Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2023, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the near-field interaction of vertically offset turbulent plumes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 966 / 10 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2023, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mega-analysis of association between obesity and cortical morphology in bipolar disorders: ENIGMA study in 2832 participants
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2023, pp. 6743-6753
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Milliarcsecond structures of variable-peaked spectrum sources
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2023, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Recreational cannabis legalization has had limited effects on a wide range of adult psychiatric and psychosocial outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2023, pp. 6481-6490
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A COMPARISON OF EXPLICIT RUNGE–KUTTA METHODS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2022, pp. 227-249
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using machine learning with intensive longitudinal data to predict depression and suicidal ideation among medical interns over time
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2022, pp. 5778-5785
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky Murchison Widefield Array survey eXtended (GLEAM-X) I: Survey description and initial data release
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2022, e035
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
102 Characterization of Hub and Spoke Facilities for Study of Surgical Care within United States Health Systems
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue s1 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Preincision versus postincision frequent door openings during total joint arthroplasty
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2022, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cervical lymphadenopathy following coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine: clinical characteristics and implications for head and neck cancer services
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 135 / Issue 11 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2021, pp. 1025-1030
- Print publication:
- November 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
ROME, PARTHIA, WAR AND PEACE - (J.M.) Schlude Rome, Parthia, and the Politics of Peace. The Origins of War in the Ancient Middle East. Pp. xvi + 221, ills, maps. London and New York: Routledge, 2020. Cased, £120, US$155. ISBN: 978-0-8153-5370-6.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 71 / Issue 2 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2021, pp. 491-493
- Print publication:
- October 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Utilizing bycatch camera-trap data for broad-scale occupancy and conservation: a case study of the brown hyaena Parahyaena brunnea
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Recommendations for Patients with Complex Nerve Injuries during the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 48 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2020, pp. 50-55
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
4146 Establishment of Screening Methods for G6DP Deficiency – Translational and Clinical Applications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue s1 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2020, p. 108
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Two cases of imported respiratory diphtheria in Edinburgh, Scotland, October 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2020, e143
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation