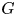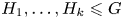743 results
106 Transforming Health Equity with an Innovative Social Determinants of Health Platform: Application of HOUSES Index to Colorectal Cancer Screening
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Development of Layer Charge and Kinetics of Experimental Smectite Alteration
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / April 1985
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 81-88
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rehydration of Zn-Al Layered Double Hydroxides
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / February 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 92-98
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evolution, culture, and the possibility of peace
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 47 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dissolution Rates of Allophane With Variable Fe Contents: Implications for Aqueous Alteration and the Preservation of X-Ray Amorphous Materials on Mars
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 263-288
-
- Article
- Export citation
3 Two Dominant Post-COVID Subtypes in Patients Seeking Treatment for “Brain Fog” Through a Post-COVID Treatment Clinic
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 876-877
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
6 Improved verbal fluency following unilateral right hemisphere subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: Is implant hemisphere a modifiable risk factor for cognitive decline?
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 112-113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Strengthening self-regulation and reducing poverty to prevent adolescent depression and anxiety: Rationale, approach and methods of the ALIVE interdisciplinary research collaboration in Colombia, Nepal and South Africa
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, e69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ten New Insights in Climate Science 2023/2024
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2023, pp. 1-58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Intersection configurations in free and free times free-abelian groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
‘PLUNDERING THE LIBERAL PHILOSOPHICAL TRADITION’? THE USE OR ABUSE OF ADAM SMITH IN PARLIAMENT, 1919–2023
-
- Journal:
- National Institute Economic Review / Volume 265 / Autumn 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, pp. 144-156
- Print publication:
- Autumn 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
MINIMALLY DESTRUCTIVE RADIOCARBON DATING OF CAPRINE DUNG
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. 832-847
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social isolation from childhood to mid-adulthood: is there an association with older brain age?
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 16 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, pp. 7874-7882
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
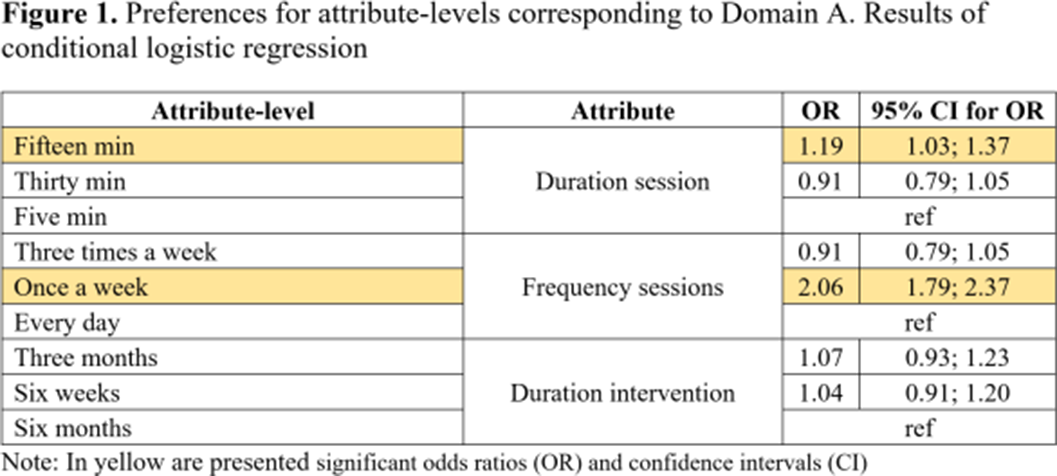
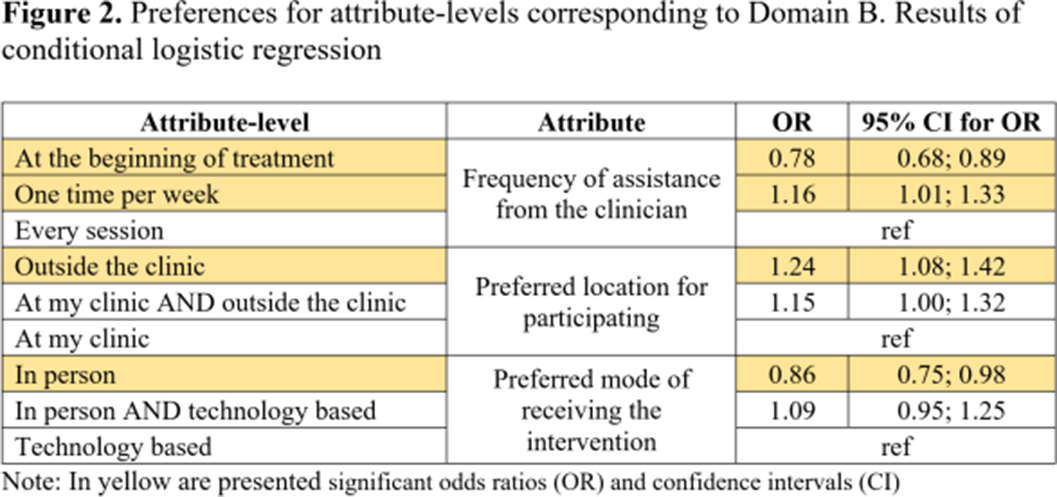
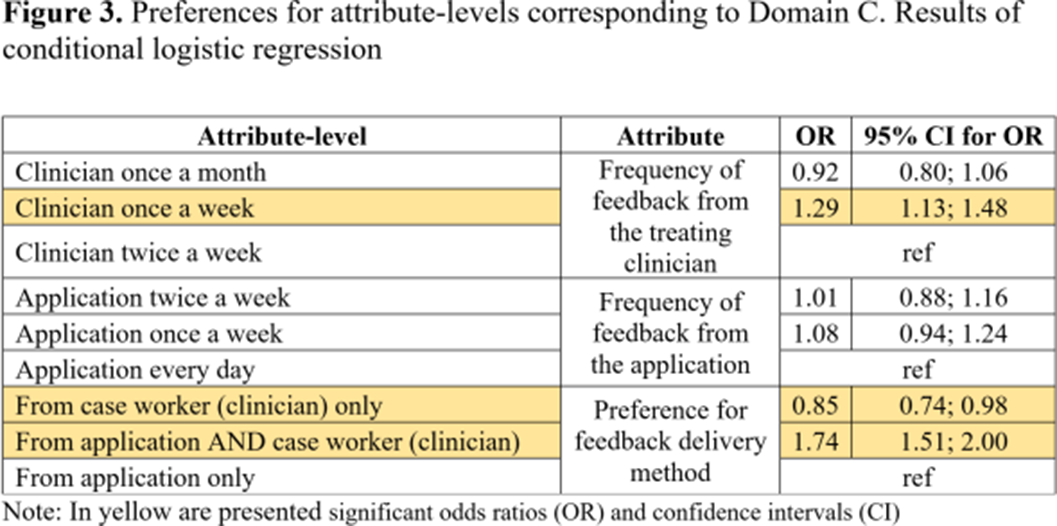
Using Best-Worst Scaling to assess preferences for online psychological interventions to decrease cannabis use in young adults with psychosis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S528-S529
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Remote and semi-automated methods to conduct a decentralized randomized clinical trial
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2023, e153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multi-Site Replications in Social Psychology: Reflections, Implications, and Future Directions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Spanish Journal of Psychology / Volume 26 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Collective Bargaining as a Minimum Employment Standard
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / July 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 153-164
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ten new insights in climate science 2022
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 5 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2022, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Part III - The Finite Volume Method
-
- Book:
- Finite Element and Finite Volume Methods for Heat Transfer and Fluid Dynamics
- Published online:
- 27 January 2023
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 215-372
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part I - Preliminaries
-
- Book:
- Finite Element and Finite Volume Methods for Heat Transfer and Fluid Dynamics
- Published online:
- 27 January 2023
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 1-90
-
- Chapter
- Export citation