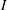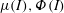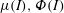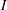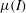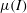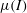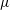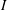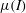138 results
Predictors of postpandemic preparedness for special pathogens
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 4 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2024, e122
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is peace a human phenomenon?
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 47 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigating the Effectiveness of Online Bioarchaeology Education through Participant Survey of a Cohort of International Adult Learners
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Archaeological Practice / Volume 11 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2023, pp. 421-433
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comparison of National Healthcare Safety Network surveillance definitions to physician review for central-line–associated bloodstream infections
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2023, pp. 2062-2064
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A survey study of the association between active utilization of National Healthcare Safety Network resources and central-line–associated bloodstream infection reporting
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2022, pp. 962-964
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sensation-seeking-related DNA methylation and the development of delinquency: A longitudinal epigenome-wide study
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2022, pp. 791-799
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Olfactory impairment in mild cognitive impairment with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 34 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2021, pp. 585-592
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Coupling rheology and segregation in granular flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 909 / 25 February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 December 2020, A22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Unheard, unseen and unprotected: DOHaD council’s call for action to protect the younger generation from the long-term effects of COVID-19
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 12 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2020, pp. 3-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Community perspectives on maternal and child health during nutrition and economic transition in sub-Saharan Africa
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 12 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2020, pp. 3710-3718
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mild cognitive impairment with Lewy bodies: neuropsychiatric supportive symptoms and cognitive profile
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 6 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2020, pp. 1147-1155
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clinical diagnosis of Lewy body dementia
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 6 / Issue 4 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2020, e61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reconciling previous DTI studies in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 22 / Issue S1 / March 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. S118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
2177 – Neuroanatomical Changes Associated With Subthreshold Depression In Adolescents
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E1340
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
POLITICAL SCIENCE, PUBLIC INTELLECTUALISM, AND PODCASTING
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2019, pp. 326-327
- Print publication:
- April 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Constitutive relations for compressible granular flow in the inertial regime
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 874 / 10 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2019, pp. 926-951
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the formation of urea in the ISM
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 363-364
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Fluorapatite-hingganite-(Y) coronas as products of fluid-induced xenotime-(Y) breakdown in the Skoddefjellet pegmatite, Svalbard
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / February 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 159-167
-
- Article
- Export citation
Partial regularisation of the incompressible 𝜇(I)-rheology for granular flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 828 / 10 October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2017, pp. 5-32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

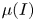
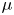
 ) which unify these currently disconnected endeavours. Coupling the segregation with the flow, and
) which unify these currently disconnected endeavours. Coupling the segregation with the flow, and