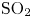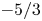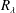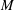57 results
Determining cut-off values and predictors for the Snaith–Hamilton Pleasure Scale: comparison between clinical and school settings
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, e106
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring the Barriers and Facilitators of Mask-Wearing Behavior During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Taiwan, the United States, the Netherlands, and Haiti: A Qualitative Study
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morbidity compression and cancer insurance
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Demographic Economics / Volume 89 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2023, pp. 465-482
-
- Article
- Export citation
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) universal admission screening in patients and companions in Taiwan from May 2021 to June 2022: A nationwide multicenter study
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, pp. 68-74
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Predator–prey interactions based on drillholes: A case study of turritelline gastropods from the Pleistocene Szekou Formation of Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh / Volume 114 / Issue 1-2 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 167-175
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Towards diverse and contextually anchored paraphrase modeling: A dataset and baselines for Finnish
-
- Journal:
- Natural Language Engineering / Volume 30 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. 319-353
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparative effectiveness of psychotherapies in adults with posttraumatic stress disorder: a network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 13 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 6376-6388
-
- Article
- Export citation
Energetics of buoyancy-generated turbulent flows with active scalar: pure buoyant plume
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 954 / 10 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2023, A23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of sleep quality on the association between problematic internet use and quality of life in people with substance use disorder
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, e155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
113 Identifying Barriers to HPV-Vaccination in the US Veteran Population
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue s1 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, pp. 4-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The impacts of maternal childhood adversity, stress, and mental health on child development at 6 months in Taiwan: A follow-up study
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2020, pp. 970-979
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Attenuated vagally-mediated heart rate variability at rest and in response to postural maneuvers in patients with generalized anxiety disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 9 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2019, pp. 1433-1441
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shock–turbulence interactions at high turbulence intensities
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 870 / 10 July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2019, pp. 813-847
-
- Article
- Export citation
2296: Functional analysis of the cutaneous microbiome in psoriatic disease
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2018, p. 15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
GADL1 variant and medication adherence in predicting response to lithium maintenance treatment in bipolar I disorder
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 2 / Issue 5 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2018, pp. 301-306
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
7 - From Double Board to Unitary Board System
- from Part II - Asian Jurisdiction-Specific Chapters
-
-
- Book:
- Independent Directors in Asia
- Published online:
- 23 October 2017
- Print publication:
- 02 November 2017, pp 241-276
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The role of basement-involved normal faults in the recent tectonics of western Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 153 / Issue 5-6 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2016, pp. 1166-1191
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social cohesion and health in old age: a study in southern Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 27 / Issue 11 / November 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2015, pp. 1903-1911
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lack of association between dopamine D3 receptor Ser9Gly polymorphism and schizophrenia in Han Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Volume 19 / Issue 6 / December 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2014, pp. 344-350
-
- Article
- Export citation
Major depression is associated with cardiac autonomic dysregulation
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Volume 24 / Issue 6 / December 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2014, pp. 318-327
-
- Article
- Export citation