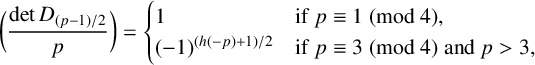181 results
SlCarE054 in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) showed direct metabolic activity to β-cypermethrin with stereoselectivity
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON GENERALISED LEGENDRE MATRICES INVOLVING ROOTS OF UNITY OVER FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics and boundary layer transition in flow around a rectangular cylinder with different aspect ratios at medium Reynolds number
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 982 / 10 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, A5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
RNA Sequencing Reveals the Differentially Expressed circRNAs between Stable and Unstable Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaques
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Distinct neurofunctional alterations during motivational and hedonic processing of natural and monetary rewards in depression – a neuroimaging meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 639-651
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late Quaternary glaciations in the Taniantaweng Mountains
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 117 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 3-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Promotion of improved intestinal barrier health by soybean-derived bioactive peptides in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) fed a low fishmeal diet
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 974-986
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Do employees dare to improvise under authoritarian leadership? A conditional indirect effect depending on relationship and task environment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A leadership model supporting maturation of high-performance translational teams
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, e171
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Integrating Logic Rules with Everything Else, Seamlessly
-
- Journal:
- Theory and Practice of Logic Programming / Volume 23 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2023, pp. 678-695
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generation of a curved plasma channel from a discharged capillary for intense laser guiding
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, e58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Three-dimensional sedimentation patterns of two interacting disks in a viscous fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 960 / 10 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, A25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Habitat selection and population status of breeding Wood Snipe Gallinago nemoricola in an alpine meadow in Sichuan, China
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2023, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anomaly Discovery and Arbitrage Trading
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 59 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2023, pp. 933-955
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
18 - UAV-Assisted Status Updates
-
-
- Book:
- Age of Information
- Published online:
- 02 February 2023
- Print publication:
- 09 February 2023, pp 456-477
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Power Transmission Network Optimization Strategy Based on Random Fractal Beetle Antenna Algorithm
-
- Journal:
- Wireless Power Transfer / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e1
- Print publication:
- 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary betaine intake and risk of mortality in patients with coronary artery disease: the prospective Guangdong Coronary Artery Disease Cohort
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2022, pp. 10-19
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation