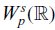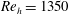51 results
MCTrans++: a 0-D model for centrifugal mirrors
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2024, 905900217
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
70 Social Anhedonia in the Daily Lives of People with Schizophrenia: Examination of Anticipated and Consummatory Pleasure
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, p. 19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
“HOW CAN I LIBERATE THE SLAVES?” THE NEGLECTED TRADITION OF DEVELOPMENTAL ABOLITIONISM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, pp. 539-558
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Non-opioid analgesics and post-operative pain following transoral robotic surgery for oropharyngeal cancer
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, pp. 527-534
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A wake-up call: playback attraction data link numbers of Mount Cameroon Francolin Pternistis camerunensis to abundance and debarking of red stinkwood Prunus africana
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 32 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2021, pp. 43-52
-
- Article
- Export citation
Well-posedness of the Muskat problem in subcritical Lp-Sobolev spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2021, pp. 224-266
-
- Article
- Export citation
Herbicide-Induced Ethylene Production: Role of the Gas in Sublethal Doses of 2,4-D
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 16 / Issue 4 / October 1968
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 498-500
-
- Article
- Export citation
Severe Influenza in 33 US Hospitals, 2013–2014: Complications and Risk Factors for Death in 507 Patients
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 36 / Issue 11 / November 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2015, pp. 1251-1260
- Print publication:
- November 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
Closed-loop separation control using machine learning
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 770 / 10 May 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2015, pp. 442-457
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nascent Regional System for Alerting Infection Preventionists about Patients with Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria: Implementation and Initial Results
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 35 / Issue S3 / October 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2016, pp. S40-S47
- Print publication:
- October 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Geriatric Emergency Medicine
- Published online:
- 05 January 2014
- Print publication:
- 16 January 2014, pp vii-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Genetic Basis of Sleep and Sleep Disorders
- Published online:
- 05 November 2013
- Print publication:
- 24 October 2013, pp xi-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
List of contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Behavioral Genetics of the Mouse
- Published online:
- 05 May 2013
- Print publication:
- 25 April 2013, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Offspring psychopathology following preconception, prenatal and postnatal maternal bereavement stress
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / January 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2013, pp. 71-84
-
- Article
- Export citation
Computational Studies of the NiTi Alloy System: Bulk, Supercell, and Surface Calculations
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1295 / 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2011, mrsf10-1295-n01-06
- Print publication:
- 2011
-
- Article
- Export citation
New heterodontosaurid specimens from the Lower Jurassic of southern Africa and the early ornithischian dinosaur radiation
-
- Journal:
- Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh / Volume 101 / Issue 3-4 / September 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2011, pp. 351-366
- Print publication:
- September 2010
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Morbid Obesity
- Published online:
- 04 May 2010
- Print publication:
- 11 March 2010, pp -
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The association between pre-morbid adjustment, duration of untreated psychosis and outcome in first-episode psychosis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue 8 / August 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2008, pp. 1157-1166
-
- Article
- Export citation
Parental mental illness and fatal birth defects in a national birth cohort
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue 10 / October 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2007, pp. 1495-1503
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of defaunation on fermentation characteristics and biotin balance in an artificial rumen-simulation system (RUSITEC) receiving diets with different amounts and types of cereal
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 95 / Issue 1 / January 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2007, pp. 99-104
- Print publication:
- January 2006
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation