89 results
Intensifying a crop–fallow system: impacts on soil properties, crop yields, and economics
-
- Journal:
- Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems / Volume 38 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2023, e42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 10 - Social Activism
- from Part II - Society
-
-
- Book:
- Chekhov in Context
- Published online:
- 16 February 2023
- Print publication:
- 23 February 2023, pp 78-84
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The Puzzles Test and the Red Shapes Test as new diagnostic tools for neglect syndrome
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S879
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Multiscale magnetic field structures in an expanding elongated plasma cloud with hot electrons subject to an external magnetic field
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2022, 175880301
-
- Article
- Export citation
20 - Experimental Syntax and Slavic Languages
- from Part III - Experimental Studies of Specific Populations and Language Families
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Experimental Syntax
- Published online:
- 16 December 2021
- Print publication:
- 09 December 2021, pp 534-560
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Challenges for quality control of institutional bone banking in developing countries
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2021, pp. 808-810
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generation of zonal flows in convective systems by travelling thermal waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 913 / 25 April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2021, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Platinum-group minerals from the Malaya Kamenushka River placer, Middle Urals, Russia
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 84 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2020, pp. 900-912
-
- Article
- Export citation
4417 Association between Brain Volumes and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Intensive Care Unit Survivors
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue s1 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2020, p. 22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Luboržákite, Mn2AsSbS5, a new member of pavonite homologous series from Vorontsovskoe gold deposit, Northern Urals, Russia
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 84 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 738-745
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inverse cascade of energy in helical turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 895 / 25 July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2020, A13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Closing the gap between training needs and training provision in addiction medicine
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych International / Volume 17 / Issue 2 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2019, pp. 37-39
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On uniqueness of transfer rates in magnetohydrodynamic turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 85 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2019, 905850507
-
- Article
- Export citation
Natrotitanite, ideally (Na0.5Y0.5)Ti(SiO4)O, a new mineral from the Verkhnee Espe deposit, Akjailyautas mountains, Eastern Kazakhstan district, Kazakhstan: description and crystal structure
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 76 / Issue 1 / February 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 37-44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fluoroleakeite, NaNa2(Mg2Fe3+2Li)Si8O22F2, a new mineral of the amphibole group from the Verkhnee Espe deposit, Akjailyautas Mountains, Eastern Kazakhstan District, Kazakhstan: description and crystal structure
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 74 / Issue 3 / June 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 521-528
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cámaraite, Ba3NaTi4(Fe2+,Mn)8(Si2O7)4O4(OH,F)7. I. A new Ti-silicate mineral from the Verkhnee Espe Deposit, Akjailyautas Mountains, Kazakhstan
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 73 / Issue 5 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 847-854
-
- Article
- Export citation
Countability, agreement and the loss of the dual in Russian
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Linguistics / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / 01 November 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2018, pp. 779-821
- Print publication:
- 01 November 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flows of measures generated by vector fields
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 148 / Issue 4 / August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2018, pp. 773-818
- Print publication:
- August 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
THREE-DIMENSIONAL ISOLATED QUOTIENT SINGULARITIES IN EVEN CHARACTERISTIC
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / May 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2017, pp. 435-445
- Print publication:
- May 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Irradiation of materials with short, intense ion pulses at NDCX-II
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2017, pp. 373-378
-
- Article
- Export citation



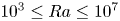
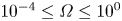
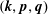

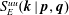
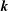
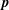
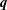
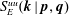
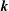
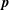
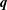
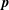
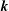
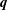
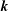
 ); 2.994, 6, (200); 1.641, 4, (330); 4.941, 3, (110); 1.498, 3, (400); 2.273, 3, (11
); 2.994, 6, (200); 1.641, 4, (330); 4.941, 3, (110); 1.498, 3, (400); 2.273, 3, (11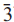 ). Chemical analysis by electron microprobe gave Nb
). Chemical analysis by electron microprobe gave Nb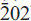 ), 2.166(20)(261), 2.325(15)(
), 2.166(20)(261), 2.325(15)( ), 2.275(15)(
), 2.275(15)(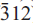 ) and 2.806(10)(330). Analysis by a combination of electron microprobe and crystal-structure refinement gives SiO
) and 2.806(10)(330). Analysis by a combination of electron microprobe and crystal-structure refinement gives SiO ,
, 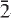
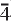 3,
3,  2); 3.39, (50), (2
2); 3.39, (50), (2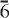
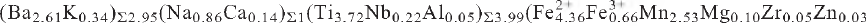 Ca
Ca