Book contents
- Treatment of Dystonia
- Treatment of Dystonia
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- 1 Development of the Concept of Dystonia as a Disease, a Syndrome and a Movement Phenomenology
- Section I Basics
- 2 Classification of Dystonia
- 3 Primary or Idiopathic Dystonias (‘Isolated Dystonia’)
- 4 Non-Primary Dystonias
- 5 Epidemiology of Dystonia
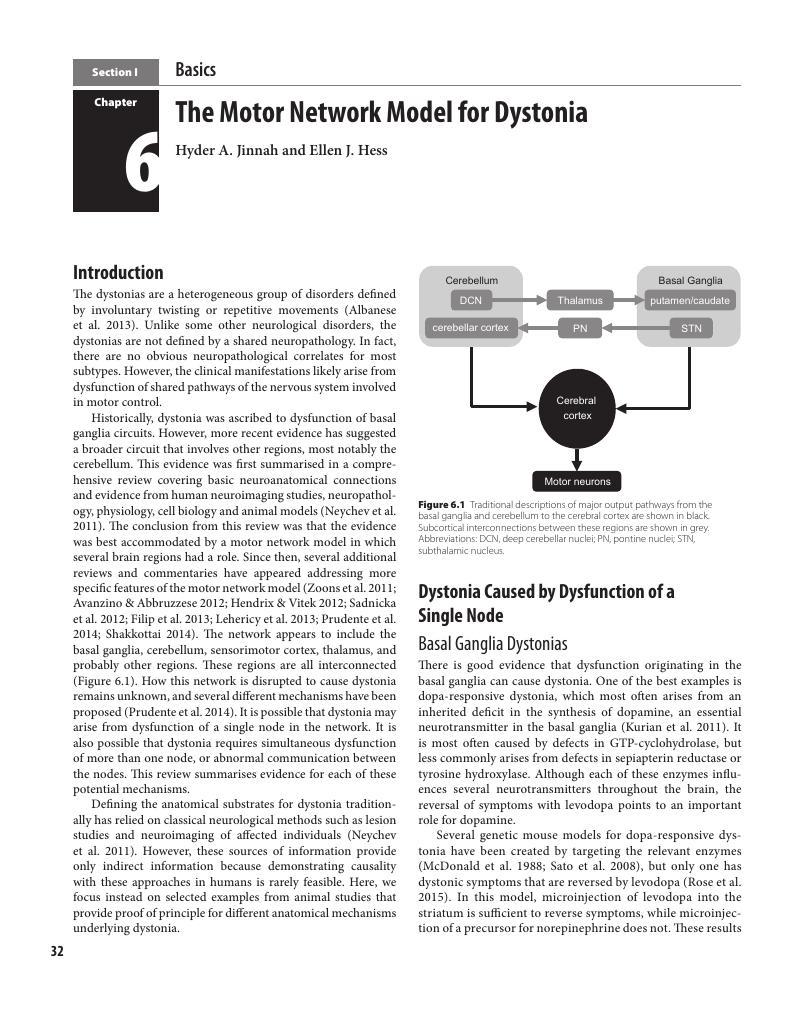
- 6 The Motor Network Model for Dystonia
- 7 Functional Imaging in Dystonia
- 8 The Pathophysiology of Dystonia
- 9 Animal Models of Dystonia
- 10 Genetics of the Dystonias
- 11 Dystonia
- 12 Dystonia and Tremor
- 13 Posttraumatic Dystonia
- 14 Non-Motor Symptoms in Dystonia
- 15 Scales for Assessment of Dystonia
- 16 Theories Behind Dystonia Scale Development
- 17 Linking Allied Health Professionals and Physicians
- 18 The Role and Responsibility of the Dystonia Specialist Nurse
- 19 History of Dystonia Treatments
- 20 Dystonia in Arts and Artists
- Section II Botulinum Toxin Therapy
- Section III Musician’s Dystonia
- Section IV Psychogenic Dystonia
- Section V Treatment of Paediatric Dystonia
- Section VI Rehabilitation of Dystonia
- Section VII Pharmacotherapy for Dystonia
- Section VIII Surgical Treatment of Dystonia
- Section IX Deep Brain Stimulation for Dystonia
- Section X Emerging Therapies for Dystonia
- Section XI Future Trends in Dystonia Therapy
- Book part
- Index
- References
6 - The Motor Network Model for Dystonia
from Section I - Basics
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 May 2018
- Treatment of Dystonia
- Treatment of Dystonia
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- 1 Development of the Concept of Dystonia as a Disease, a Syndrome and a Movement Phenomenology
- Section I Basics
- 2 Classification of Dystonia
- 3 Primary or Idiopathic Dystonias (‘Isolated Dystonia’)
- 4 Non-Primary Dystonias
- 5 Epidemiology of Dystonia
- 6 The Motor Network Model for Dystonia
- 7 Functional Imaging in Dystonia
- 8 The Pathophysiology of Dystonia
- 9 Animal Models of Dystonia
- 10 Genetics of the Dystonias
- 11 Dystonia
- 12 Dystonia and Tremor
- 13 Posttraumatic Dystonia
- 14 Non-Motor Symptoms in Dystonia
- 15 Scales for Assessment of Dystonia
- 16 Theories Behind Dystonia Scale Development
- 17 Linking Allied Health Professionals and Physicians
- 18 The Role and Responsibility of the Dystonia Specialist Nurse
- 19 History of Dystonia Treatments
- 20 Dystonia in Arts and Artists
- Section II Botulinum Toxin Therapy
- Section III Musician’s Dystonia
- Section IV Psychogenic Dystonia
- Section V Treatment of Paediatric Dystonia
- Section VI Rehabilitation of Dystonia
- Section VII Pharmacotherapy for Dystonia
- Section VIII Surgical Treatment of Dystonia
- Section IX Deep Brain Stimulation for Dystonia
- Section X Emerging Therapies for Dystonia
- Section XI Future Trends in Dystonia Therapy
- Book part
- Index
- References
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Treatment of Dystonia , pp. 32 - 35Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2018
References
- 1
- Cited by



