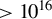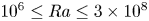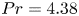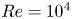265 results
Generation of polarized electron beams through self-injection in the interaction of a laser with a pre-polarized plasma
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linked patterns of symptoms and cognition with brain controllability in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S420
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A machine learning model for predicting the three-year survival status of patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma using multiple parameters
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2023, pp. 1041-1047
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A systematic study on 33 gallbladder stones resembling adult Clonorchis sinensis worms
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 96 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2022, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Should mild obstructive sleep apnoea be treated? A systematic review from the standpoint of disease progression
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2022, pp. 828-839
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Brain controllability and clinical relevance in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S196
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
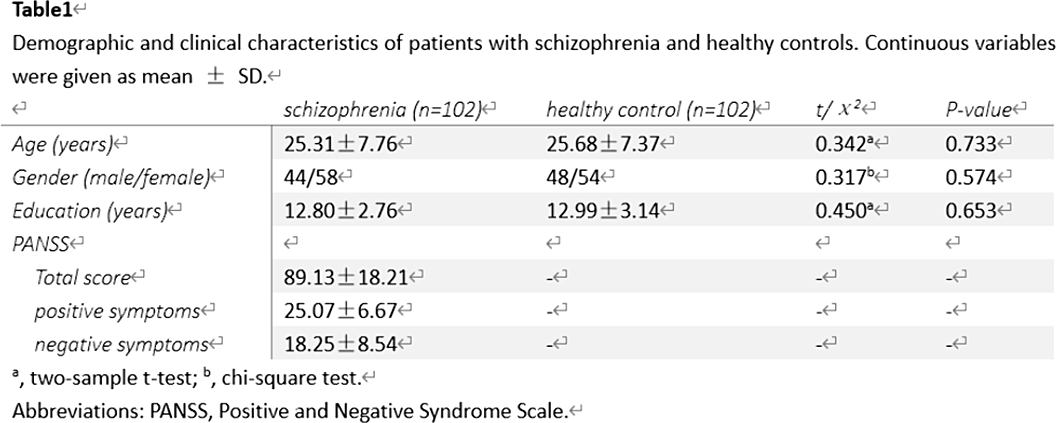
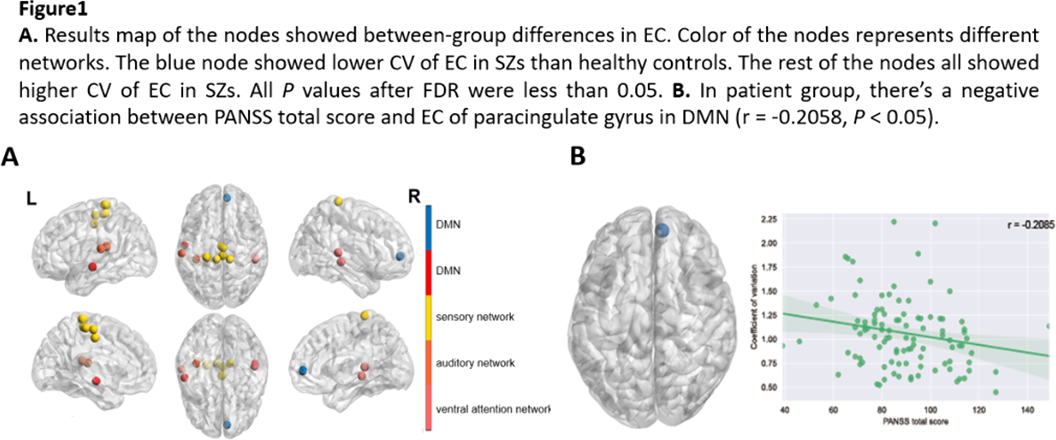
Altered dynamic functional topology in first-episode untreated patients with schizophrenia can aid in early diagnosis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S115
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Remote Assessment of Disease and Relapse in Major Depressive Disorder (RADAR-MDD): Recruitment, retention, and data availability in a longitudinal remote measurement study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acceleration of 60 MeV proton beams in the commissioning experiment of the SULF-10 PW laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Forecasting the monthly incidence of scarlet fever in Chongqing, China using the SARIMA model
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2022, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spatial epidemiological characteristics and exponential smoothing model application of tuberculosis in Qinghai Plateau, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2022, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
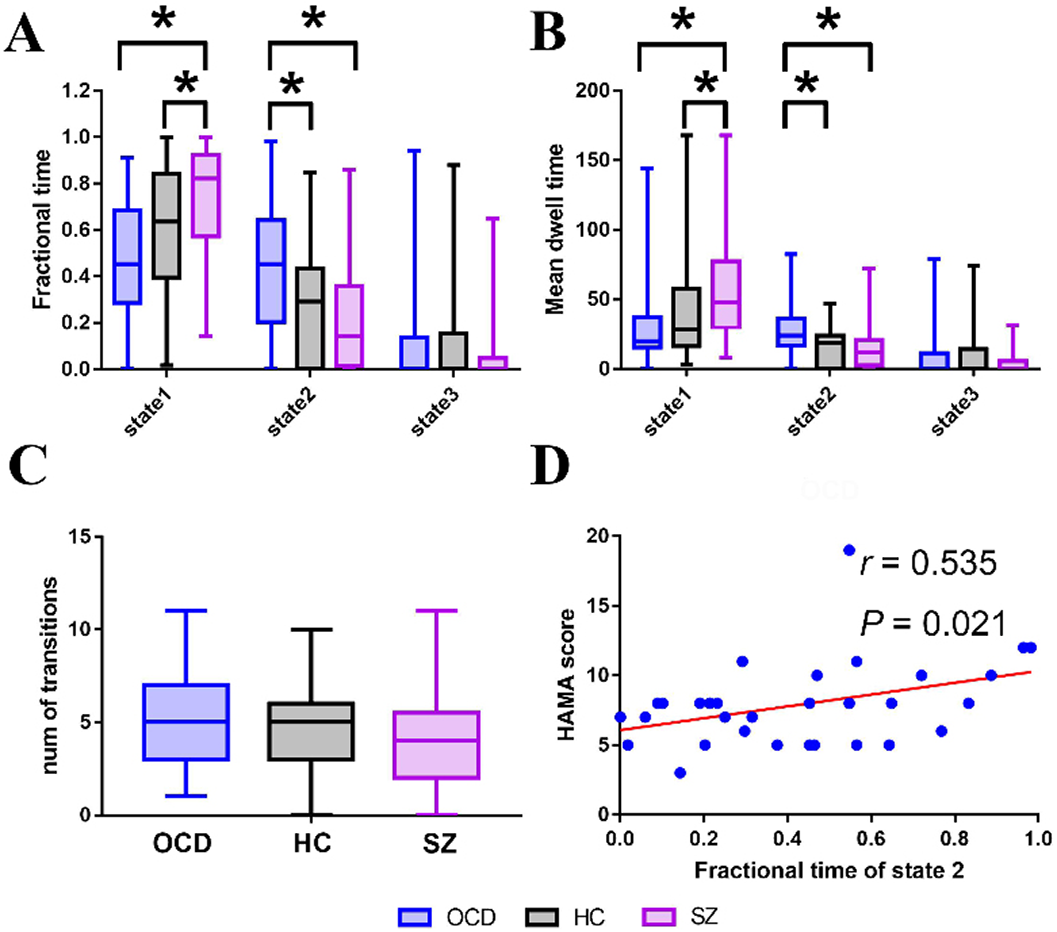
Different alternations of static and dynamic brain regional topological metrics in schizophrenia and obsessive-compulsive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. S522-S523
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Distinct alternations of brain functional network dynamics in obsessive-compulsive disorder and schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. S160-S161
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Flow structures and heat transport in Taylor–Couette systems with axial temperature gradient
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 920 / 10 August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 June 2021, A42
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of wheat powdery mildew on grain nitrogen metabolism
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 159 / Issue 1-2 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2021, pp. 128-138
-
- Article
- Export citation
The impact of COVID-19 on subthreshold depressive symptoms: a longitudinal study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 30 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2021, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA load dynamics in the nasopharynx of infected children
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2021, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of the frequency of mutation genes in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) strains in Beijing, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2021, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation