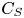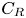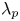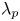284 results
Investigation of free surface effect on the cavity expansion and contraction in high-speed water entry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2024, A53
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An online method for ship trajectory compression using AIS data
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Integral methods for friction decomposition and their extensions to rough-wall flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, A46
-
- Article
- Export citation
Precise mode control of mid-infrared high-power laser diode using on-chip advanced sawtooth waveguide designs
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Dimensional homogeneity constrained gene expression programming for discovering governing equations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, A12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multidimensional credibility: A new approach based on joint distribution function
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of dietary selenium intake on CVD: a retrospective cohort study based on China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) data
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, e122
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The small heat shock protein Hsp20.8 imparts tolerance to high temperatures in the leafminer fly, Liriomyza trifolii (Diptera: Agtomyzidae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, pp. 230-236
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unveiling the Intricacies of the Inner Ear Anatomy: Novel 3D-Printed Model for Detailed Visualization and Functional Demonstrations
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of cross-language orthography and phonology in translation recognition: an ERP study with Chinese–English bilinguals
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimising cervical cancer screening during pregnancy: a study of liquid-based cytology and HPV DNA co-test
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2024, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alpha-Particle Generation from H-11B Fusion Initiated by Laser-Accelerated Boron Ions
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Transport and Exchange Behavior of Ions in Bentonite During Electro-Osmotic Consolidation
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 63 / Issue 5 / October 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 395-403
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thiourea-Induced Change of Structure and Color of Brick-Red Palygorskite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 5 / October 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 403-414
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation Of Zinc-Bearing Palygorskite Effects on Growth Performance, Nutrient Retention, Meat Quality, and Zinc Accumulation in Blunt Snout Bream Megalobrama Amblycephala
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 274-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prospect of ultrahigh-resolution fast neutron absorption spectroscopy based on a laser plasma electron accelerator
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anatomical studies and early results on endoscopic transoral medial pterygomandibular fold approach to salvage retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 540-547
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gray matter atrophy is constrained by normal structural brain network architecture in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1318-1328
-
- Article
- Export citation
The positive influence of ideological and political education on the mental health of college students
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation