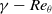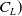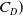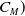667 results
Impact of elevated body mass index (BMI) on cognitive functioning and inflammation in persons with post-COVID-19 condition: a secondary analysis
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Larval anisakid infections of some tropical fish species from north-west Australia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 77 / Issue 4 / December 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 363-365
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factors that mediate change in creatinine and acute kidney injury after the Norwood operation: insights from high-fidelity haemodynamic monitoring data
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Crystal structure and synchrotron X-ray powder reference pattern for the porous pillared cyanonickelate, Ni(3-amino-4,4′-bipyridine)[Ni(CN)4]
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, pp. 20-28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tropical vegetation productivity and atmospheric methane over the last 40,000 years from model simulations and stalagmites in Sulawesi, Indonesia
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 118 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2024, pp. 126-141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P19: Effects of a Post-diagnostic Support Programme on self-efficacy among persons with dementia and family members
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 194-195
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P20: Effects of Transitional Care Program on Reducing Nursing Home Placement in People with Dementia
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 195-196
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Numerical investigation of the dynamic stall reduction on the UAS-S45 aerofoil using the optimised aerofoil method
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1321 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 441-468
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of external magnetic field and dust grains on the properties of ion-acoustic waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2023, 905890502
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Mopra Southern Galactic Plane CO Survey – data release 4– complete survey
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 11 - Ischemic Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack
- from Section 3 - Specific Neurological Disorders in Emergency Medicine
-
-
- Book:
- Handbook of Emergency Neurology
- Published online:
- 10 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 August 2023, pp 137-172
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Whole-genome sequencing rule-out of suspected hospital-onset Rhizopus outbreaks
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, pp. 2059-2061
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of maternal exposure to Superstorm Sandy and maternal cannabis use with development of psychopathology among offspring: the Stress in Pregnancy Study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2023, e94
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pre-pilot survey: Radio continuum properties of the Eridanus supergroup
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, e012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of energy restriction with and without almonds on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of 3 months of energy restriction on serum lipids and lipoprotein responses in overweight adults
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E109
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Are fewer cases of diabetes mellitus diagnosed in the months after SARS-CoV-2 infection? A population-level view in the EHR-based RECOVER program
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in patients with spinal cord injury at admission to hospital: a single centre study in the UK
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, E15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
James Sharpe’s Contributions to Neurology and Neuro-ophthalmology: A Posthumous Tribute 10 Years On
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2023, pp. 117-121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation