50 results
Investigating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on recovery colleges: multi-site qualitative study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, e113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deferring to Expertise whilst Maintaining Autonomy
-
- Journal:
- Episteme , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The predictive role of symptoms in COVID-19 diagnostic models: A longitudinal insight
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
48 Associations Between Cognitive Function and Social Networks in Older Adults: Quality and not Quantity?
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 834-835
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
25 Specific Facets of Trait Mindfulness Show Differences in Associations with Affective and Cognitive Measures in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 338
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
52 Association Between COVID-19 Coping Strategies and Cognitive Function in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 360
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
6 Now or Later? Decision-Making Preferences in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 321-322
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Evaluation of a menu box delivery service for Australian long-day care services to improve food provision and child intake: a cluster randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2023, pp. 3122-3133
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“More effective” is not necessarily “better”: Some ethical considerations when influencing individual behaviour
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 46 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, e151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
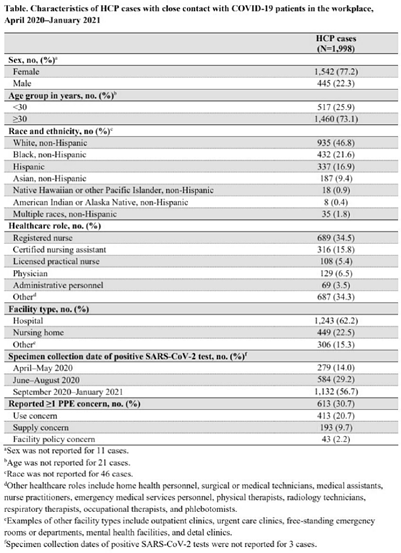
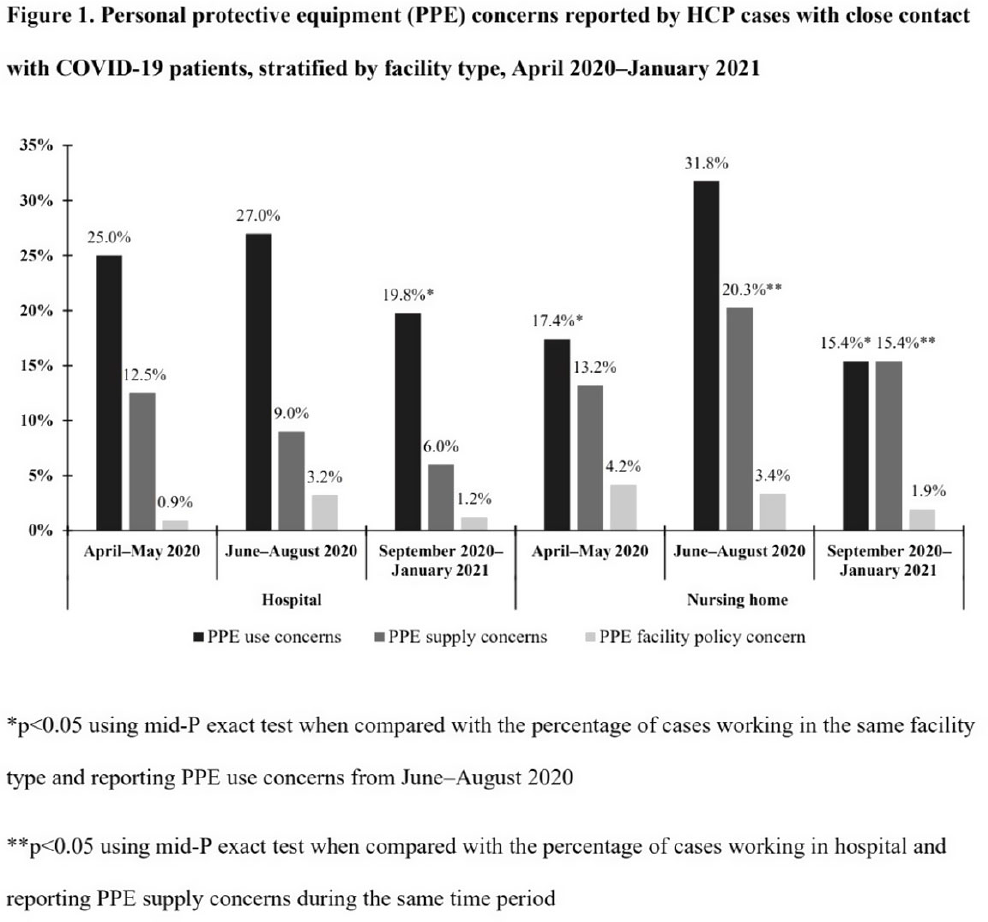
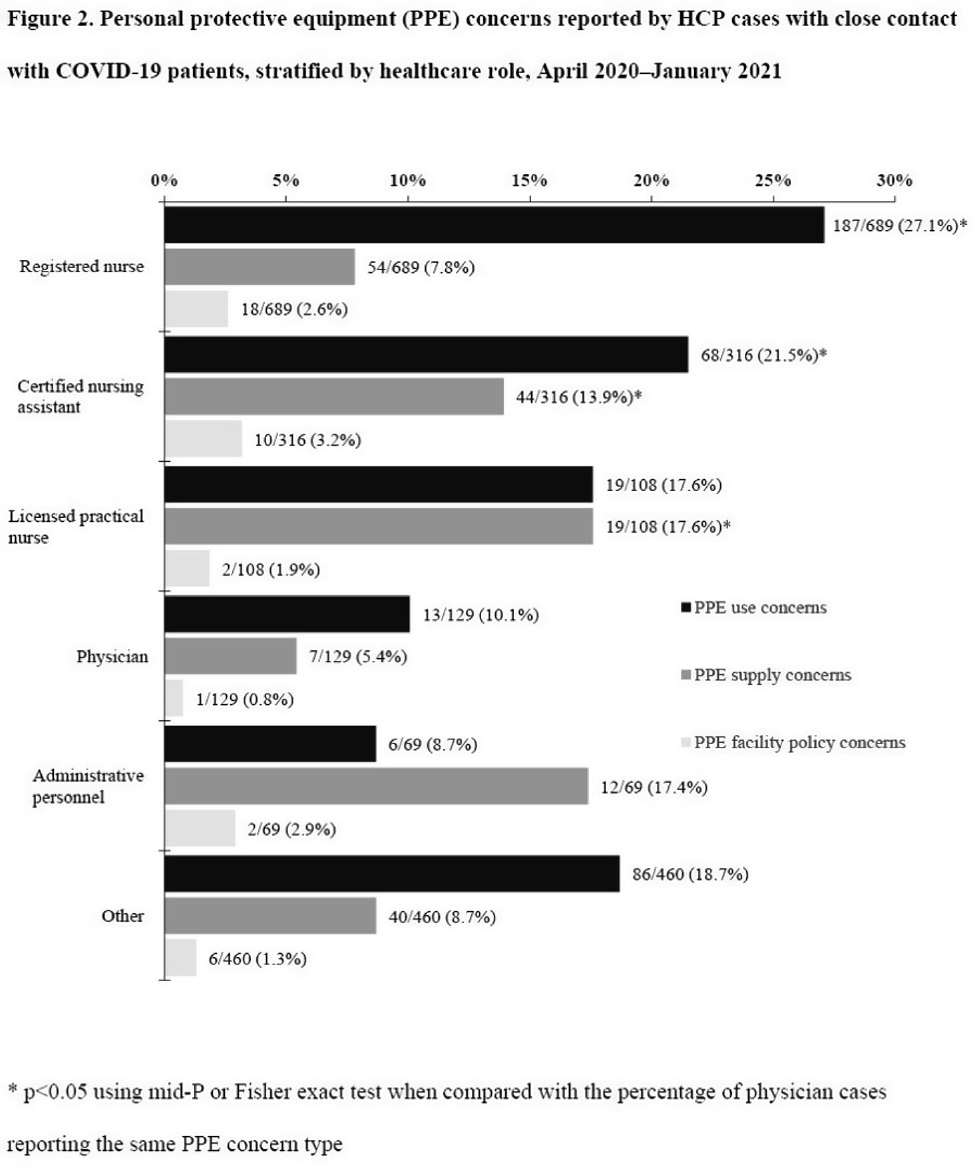
Characteristics of healthcare personnel who reported concerns related to PPE use during care of COVID-19 patients
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, pp. s8-s9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Revisiting ‘Toledo, Rome, and the Legacy of Gaul’: new evidence from the Divine Office
-
- Journal:
- Plainsong & Medieval Music / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 April 2022, pp. 1-35
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
10 - The Developmental Science of Politics
- from Part I - Foundations of Political Psychology
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Political Psychology
- Published online:
- 17 February 2022
- Print publication:
- 24 February 2022, pp 159-174
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Parents’ decision-making for their foetus or neonate with a severe congenital heart defect
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, pp. 896-903
-
- Article
- Export citation
Virtual balint group experience due to the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue S1 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2021, pp. S127-S128
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Trends in referrals to liaison psychiatry teams from UK emergency departments for patients over 65
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue S1 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2021, pp. S311-S312
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Practices and activities among healthcare personnel with severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection working in different healthcare settings—ten Emerging Infections Program sites, April–November 2020
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2021, pp. 1058-1062
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
4281 Developing a predictive tool to detect peripheral artery disease (PAD): Examining patient-reported symptoms in ischemic versus non-ischemic conditions (PREDICT PAD)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue s1 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2020, p. 27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Text Messaging and Disaster Preparedness Aids Engagement, Re-Engagement, Retention, and Communication Among Puerto Rican Participants in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Self-Testing Study After Hurricanes Irma and Maria
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2020, e2
-
- Article
- Export citation
In vitro screening of 51 birdsfoot trefoil (Lotus corniculatus L.; Fabaceae) strains for anti-parasitic effects against Haemonchus contortus
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 146 / Issue 6 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2019, pp. 828-836
-
- Article
- Export citation
2085: MyResearchHome@Duke—launch and adoption of a portal for the research community
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2018, p. 11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation