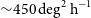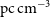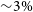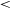141 results
Effects of dietary nitrate supplementation on markers of oral health: A systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 83 / Issue OCE2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2024, E210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Interactive visualization tool to understand and monitor health disparities in diabetes care and outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2024, e102
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neurosurgical Operative Cancellations in Canada: A Multicentre Retrospective Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessments and observations of infection prevention and control practices in US outpatient hemodialysis facilities, 2015–2018: important opportunities for improvement
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of residential acaricide treatments on patterns of pathogen coinfection in blacklegged ticks
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dose-response relationships of seven dietary patterns with incident type 2 diabetes: Findings from the UK Biobank study
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E313
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
42 Associations Between Mild Traumatic Brain Injury, Executive Function, and Criminal Justice Involvement among Veterans and Service Members: a LIMBIC-CENC study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 148-150
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
11 - Collaboration
- from Part III - Collecting and Analysing Data
-
-
- Book:
- Conducting Research on Global Environmental Agreement-Making
- Published online:
- 07 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 10 August 2023, pp 210-227
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A leadership model supporting maturation of high-performance translational teams
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, e171
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—II. Survey status, pulsar census, and first pulsar discoveries – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pliocene–Pleistocene hydrology and pluvial lake during Marine Isotope Stages 5a and 4, Deep Springs Valley, western Great Basin, Inyo County, California
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 115 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2023, pp. 160-178
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Approaches for enhancing the informativeness and quality of clinical trials: Innovations and principles for implementing multicenter trials from the Trial Innovation Network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, e131
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Temporal development of high-performance translational teams
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, e117
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—II. Survey status, pulsar census, and first pulsar discoveries
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, e020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—I. Survey design and processing pipeline
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, e021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cultural Resource Damage Assessment
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Archaeological Practice / Volume 11 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2023, pp. 111-125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Electronic surveillance criteria for non–ventilator-associated hospital-acquired pneumonia: Assessment of reliability and validity
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 11 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2023, pp. 1769-1775
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Win–win interactions: Results and implications of a user needs assessment of clinical and translational scientists
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2023, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Patterns of enteric infections in a population-wide cohort study of sequelae, British Columbia, Canada
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2022, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Different trajectories of depression, anxiety and anhedonia symptoms in the first 12 months of the COVID-19 pandemic in a UK longitudinal sample
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 December 2022, pp. 6524-6534
-
- Article
- Export citation