357 results

Intellectual Property, Innovation and Economic Inequality
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- September 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Lesbians, Gays, and Bisexuals Asset-based Welfare and Housing in Great Britain
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
HETEROSKEDASTICITY ROBUST SPECIFICATION TESTING IN SPATIAL AUTOREGRESSION
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, pp. 1-49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Alliance of protected areas for better landscape conservation outcomes in northern Saudi Arabia
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence and distribution of contralateral lymph node metastasis associated with HPV-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Higher-order CBT skills: are there differences in meta-competence between trainee and experienced therapists?
-
- Journal:
- The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist / Volume 17 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Attitudes toward automation and the demand for policies addressing job loss: the effects of information about trade-offs
-
- Journal:
- Political Science Research and Methods , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 25 - Policy to Practice
-
-
- Book:
- Seminars in Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry
- Published online:
- 04 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 18 January 2024, pp 401-412
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Editorial: Developing research potential in the primary and community-nursing workforce: the impact of a community of practice
-
- Journal:
- Primary Health Care Research & Development / Volume 24 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, e64
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
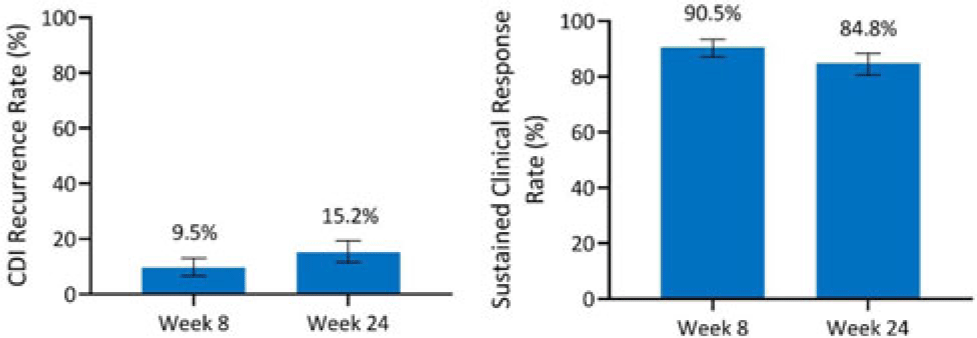
Integrated efficacy analysis from phase 3 studies of investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Impact of selection bias on polygenic risk score estimates in healthcare settings
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 15 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, pp. 7435-7445
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blood culture procedures and practices in the neonatal intensive care unit: A survey of a large multicenter collaborative in California
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 10 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. 1576-1581
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A systematic review of in-patient psychiatric care for people with intellectual disabilities and/or autism: effectiveness, patient safety and experience
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2022, e187
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Omega results for cubic field counts via lower-order terms in the one-level density
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2022, e80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Scotland's first farmers: new insights into early farming practices in North-west Europe
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TESOL teacher educators in higher education: A review of studies from 2010 to 2020
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching / Volume 55 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2022, pp. 434-469
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
3D Structural Determination of Core-shell Nanoparticles
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, p. 216
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Mental health in young adults born extremely preterm or extremely low birthweight with contemporary neonatal intensive care
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 11 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 5227-5234
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spatial Decorrelation of Ceria Surface Reduction and Platinum Surface Loading Site
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2426-2428
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cost-effectiveness of mirtazapine for agitated behaviors in dementia: findings from a randomized controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2022, pp. 905-917
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation