68 results
Suicidality and social cognition: the association between hypomentalizing and suicide lethality
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, p. S183
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Association between loneliness in childhood and first-episode psychosis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue S1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, pp. S88-S89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Group psychotherapy for patients with first-episode psychosis: Effect on the clinical status and use of resources
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S635-S636
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
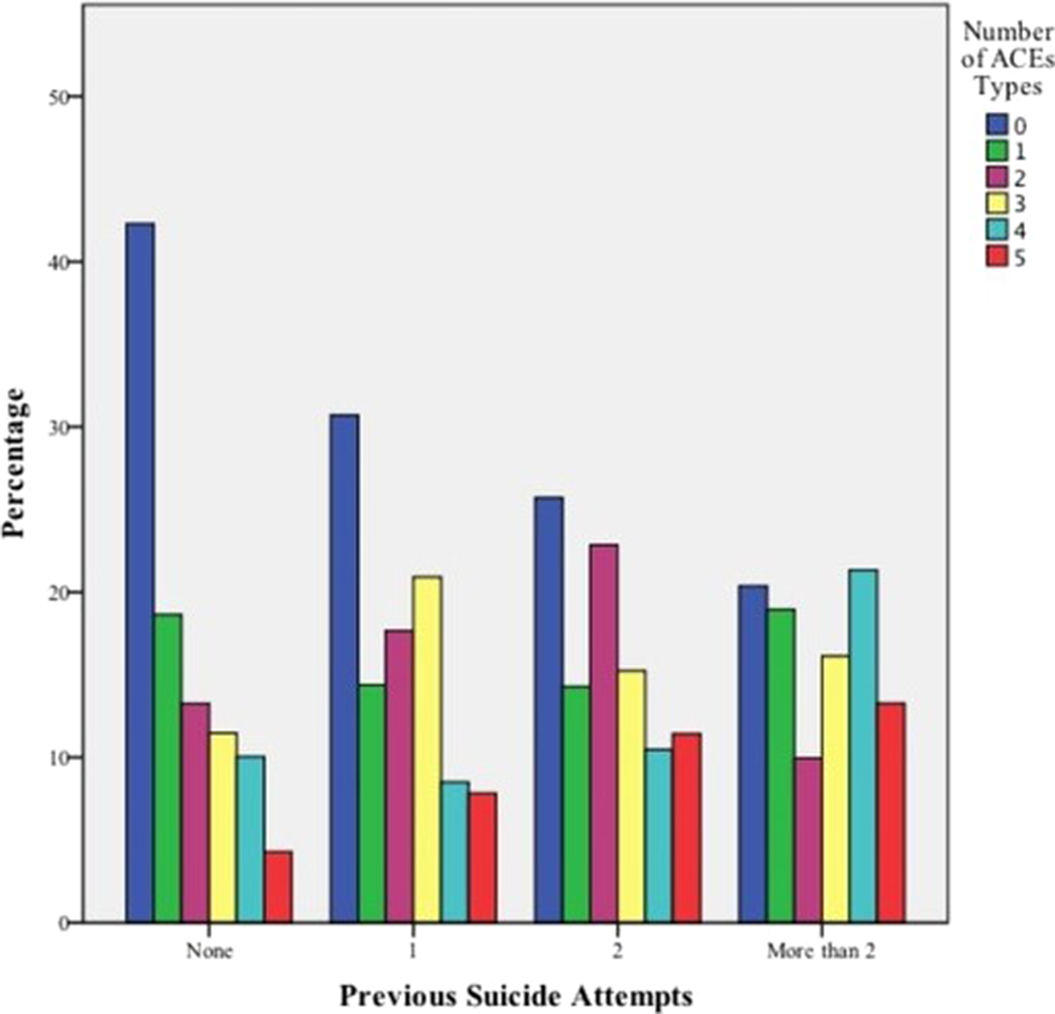
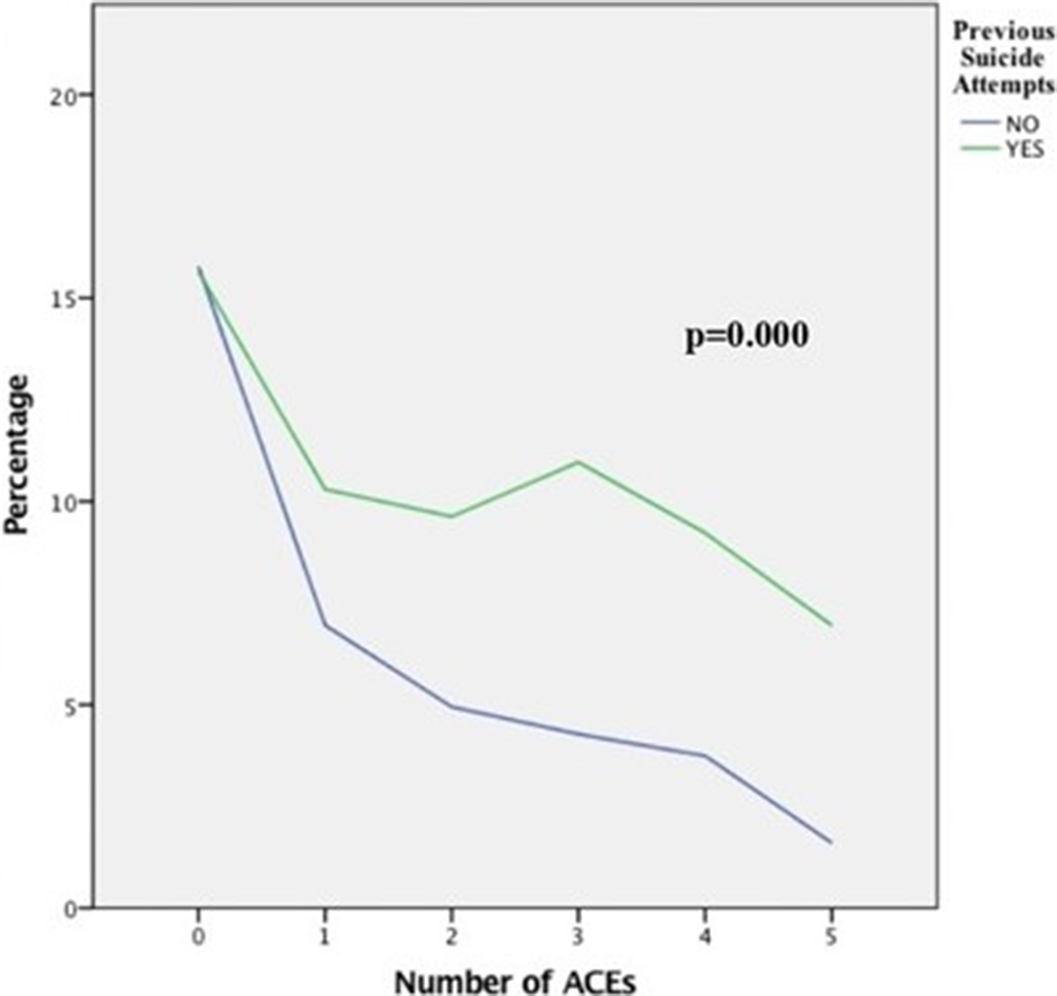
Association between adverse childhood experiences and the number of suicide attempts in lifetime
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S561-S562
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Intelligence Quotient changes over 10 years: diversity of cognitive profiles in first episode of psychosis and healthy controls
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S630
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Psychotic disorders in young patients with Prader-Willi syndrome: A case report and literature review
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S395
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Efficacy and safety of a 4-week course of repeated subcutaneous ketamine injections for treatment-resistant depression (KADS study): randomised double-blind active-controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2023, pp. 533-541
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
LINKING RADIOCARBON AND TROPHIC WEBS IN KARSTIC GROUNDWATER ECOSYSTEMS IN THE YUCATAN PENINSULA, MÉXICO
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 64 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2023, pp. 1629-1639
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Metazoan parasites of some meso- and bathypelagic fish from the Perdido region, southern Gulf of Mexico
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 102 / Issue 6 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2022, pp. 391-401
-
- Article
- Export citation
Differences in physical activity in subjects with psychosis versus a control group
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S763
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Pattern of long-term weight and metabolic changes after a first episode of psychosis: Results from a 10-year prospective follow-up of the PAFIP program for early intervention in psychosis cohort
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2022, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Immune cell arrival kinetics to peritoneum and role during murine-experimental trichomoniasis
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 148 / Issue 13 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2021, pp. 1624-1635
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mineralization of bagged pruning waste in agrosystem on the subtropical coast of Andalusia (Spain)
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 158 / Issue 8-9 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2021, pp. 634-645
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compulsory admissions of patients with mental disorders: State of the art on ethical and legislative aspects in 40 European countries
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, e82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PW01-243 - The Apomorphine Test As A Biological Marker For Relapse In Cocaine Dependent-Patients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 25 / Issue S1 / 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, 25-E1650
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PW01-141 - Brain Dysfunction In Schizomanic Patients Versus Healthy Controls: A Fmri Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 25 / Issue S1 / 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, 25-E1540
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P0194 - Profile of patients under involuntary outpatient treatment in the province of Gipuzkoa (Basque Country, Spain)
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 23 / Issue S2 / April 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. S138
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Alexithymia and Psychopathology: An 18 Month Follow-Up
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 12 / Issue S2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 225s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
New evidence of heterogeneity in social anxiety disorder: Defining two qualitatively different personality profiles taking into account clinical, environmental and genetic factors
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 160-165
-
- Article
- Export citation