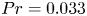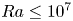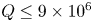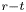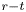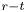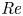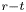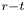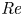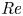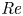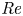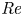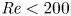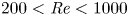162 results
Coexistence of dual wing–wake interaction mechanisms during the rapid rotation of flapping wings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Incubation experiments using nitrogen isotope discrimination to estimate ammonia emission from amended sheep manure treatments
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 67-76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of horizontal magnetic fields on turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a cuboid vessel with aspect ratio Γ = 5
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A24
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Clinical Relevance and Functional Implications of Thymosin Beta-10 in Glioma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparation and Characterization of Halloysite-Based Carriers for Quercetin Loading and Release
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 94-104
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multi-scale flow structure and its effect on momentum flux in the coastal marine atmospheric boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- Flow: Applications of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 3 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2023, E29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A KNOWLEDGE-BASED IDEATION APPROACH FOR BIO-INSPIRED DESIGN
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, pp. 231-240
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Generation of a curved plasma channel from a discharged capillary for intense laser guiding
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, e58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dual-stage radial–tangential vortex tilting reverses radial vorticity and contributes to leading-edge vortex stability on revolving wings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 963 / 25 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, A29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Computerized-adaptive testing versus short forms for pediatric inflammatory bowel disease patient-reported outcome assessment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, e109
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 10 - Incorporating the Extended Theory of Planned Behaviour in a School Travel Mode Choice Model: A Case Study of Shaoxing, China
-
-
- Book:
- School Journey as a Third Place
- Published by:
- Anthem Press
- Published online:
- 14 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 07 March 2023, pp 213-238
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Patterns of brain dynamic functional connectivity are linked with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-related behavioral and cognitive dimensions
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2023, pp. 6666-6677
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mineral textures, mineral chemistry and S isotopes of sulphides from the Tianbaoshan Pb–Zn–Cu deposit in the Sichuan–Yunnan–Guizhou triangle: implications for mineralization process
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 December 2022, pp. 471-489
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality in patients with COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, e106
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of dietary patterns with obesity and metabolically healthy obesity phenotype in Chinese population: a cross-sectional analysis of China Multi-Ethnic Cohort Study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 11 / 14 December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, pp. 2230-2240
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of Reynolds number on leading-edge vortex formation dynamics and stability in revolving wings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 931 / 25 January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2021, A13
-
- Article
- Export citation
The performance of Cobas HPV test for cervical cancer screening in Chinese female migrant workers
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2021, e196
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Emergent chirality in a polar meron to skyrmion transition revealed by 4D-STEM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 348-350
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Executive functioning in body dysmorphic disorder and obsessive–compulsive disorder
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2021, pp. 33-40
-
- Article
- Export citation
Are dietary factors involved in the association of CDH4 methylation and breast cancer risk?
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2021, pp. 1868-1877
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation