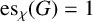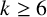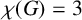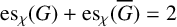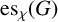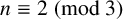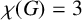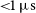66 results
Biochemical and immunological characterization of excretory–secretory products of Vesicocoelium solenophagum and plasma proteins of its bivalve host, Sinonovacula constricta
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 75 / Issue 3 / September 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 279-284
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of dietary selenium intake on CVD: a retrospective cohort study based on China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) data
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, e122
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
First international training course on conservation of Plant Species with Extremely Small Populations
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Parkes Pulsar Timing Array third data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e049
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Erythrocyte membrane n-3 PUFA are inversely associated with breast cancer risk among Chinese women
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2023, pp. 103-112
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
When uncertainty meets life: The effect of animacy on probability expression
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 8 / Issue 4 / July 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 425-438
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Getting The Message of The New ‘Family Values Clause’
-
-
- Book:
- Family Matters
- Published by:
- Intersentia
- Published online:
- 20 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 22 September 2022, pp 227-244
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Copy number variation of WBP1L gene revealed its association with growth traits across Chinese cattle populations
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2022, pp. 528-534
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
SOME EXTREMAL RESULTS ON THE CHROMATIC STABILITY INDEX
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 106 / Issue 2 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2022, pp. 185-194
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
CYP4CJ6-mediated resistance to two neonicotinoid insecticides in Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2022, pp. 646-655
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relapse risk revealed by degree centrality and cluster analysis in heroin addicts undergoing methadone maintenance treatment
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2021, pp. 2216-2228
-
- Article
- Export citation
Suicide rates among people with serious mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 2 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2021, pp. 351-361
-
- Article
- Export citation
7 - Random Matrix Theory for Analyzing Spatio-Temporal Data
- from Part II - Data-Driven Anomaly Detection
-
-
- Book:
- Advanced Data Analytics for Power Systems
- Published online:
- 22 March 2021
- Print publication:
- 08 April 2021, pp 144-174
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Natural fractures in tight gas sandstones: a case study of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang gas field, Western Sichuan Basin, China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 158 / Issue 9 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2021, pp. 1543-1560
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accuracy of high-order lattice Boltzmann method for non-equilibrium gas flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 907 / 25 January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 November 2020, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of TLR3 (rs3775291) and IL-10 (rs1800871) gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to Hepatitis B infection: A meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2020, e228
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Royal Free Hospital-Nutritional Prioritizing Tool improves the prediction of malnutrition risk outcomes in liver cirrhosis patients compared with Nutritional Risk Screening 2002
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 12 / 28 December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2020, pp. 1293-1302
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of antidepressant medicines on preventing relapse of unipolar depression: a pooled analysis of parametric survival curves
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2020, pp. 48-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Parkes Pulsar Timing Array project: second data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2020, e020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation