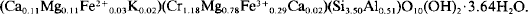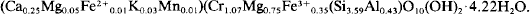103 results
177 Placing Participant Experiences at the Center of Improving Research by Empowering the Participant Voice
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 53
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Reassessment of the Volkonskoite-Chromian Smectite Nomenclature Problem: Reply
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 36 / Issue 6 / December 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, p. 541
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reassessment of the Volkonskoite-Chromian Smectite Nomenclature Problem
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / April 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 139-149
-
- Article
- Export citation
Empowering the Participant Voice (EPV): Design and implementation of collaborative infrastructure to collect research participant experience feedback at scale
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2024, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The fragility index: how robust are the outcomes of head and neck cancer randomised, controlled trials?
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 451-456
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
7 - Racism, Policing and the Pandemic
-
-
- Book:
- Crime, Justice and COVID-19
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 20 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 May 2023, pp 137-149
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
143 Wouldn’t you like to know what your research study participants are thinking? A collaboration for Empowering the Participant Voice
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 43-44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Associations between clinically diagnosed medical conditions and dietary supplement use: the US military dietary supplement use study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2023, pp. 1238-1253
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 6 - Gender, Masculinity and Cross-Dressing
- from Part I - Socio-Political Context
-
-
- Book:
- Molière in Context
- Published online:
- 10 November 2022
- Print publication:
- 24 November 2022, pp 60-68
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A social practice theory approach to exploring the ubiquity of quizzes in dementia care settings
-
- Journal:
- Ageing & Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2022, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Increased Blood Brain Barrier Permeability in the Visual Cortex of the HIV-1Transgenic Rat
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2950-2951
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Identification of Increased Blood Brain Barrier Permeability in the Substantia Nigra of the HIV-1 Transgenic Rat
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 3214-3215
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
471 Empowering the Participant Voice (EPV): Participant Feedback to Improve the Clinical Research Enterprise
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue s1 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, p. 93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Barriers and solutions to developing and maintaining research networks during a pandemic: An example from the iELEVATE perinatal network
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2022, e56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
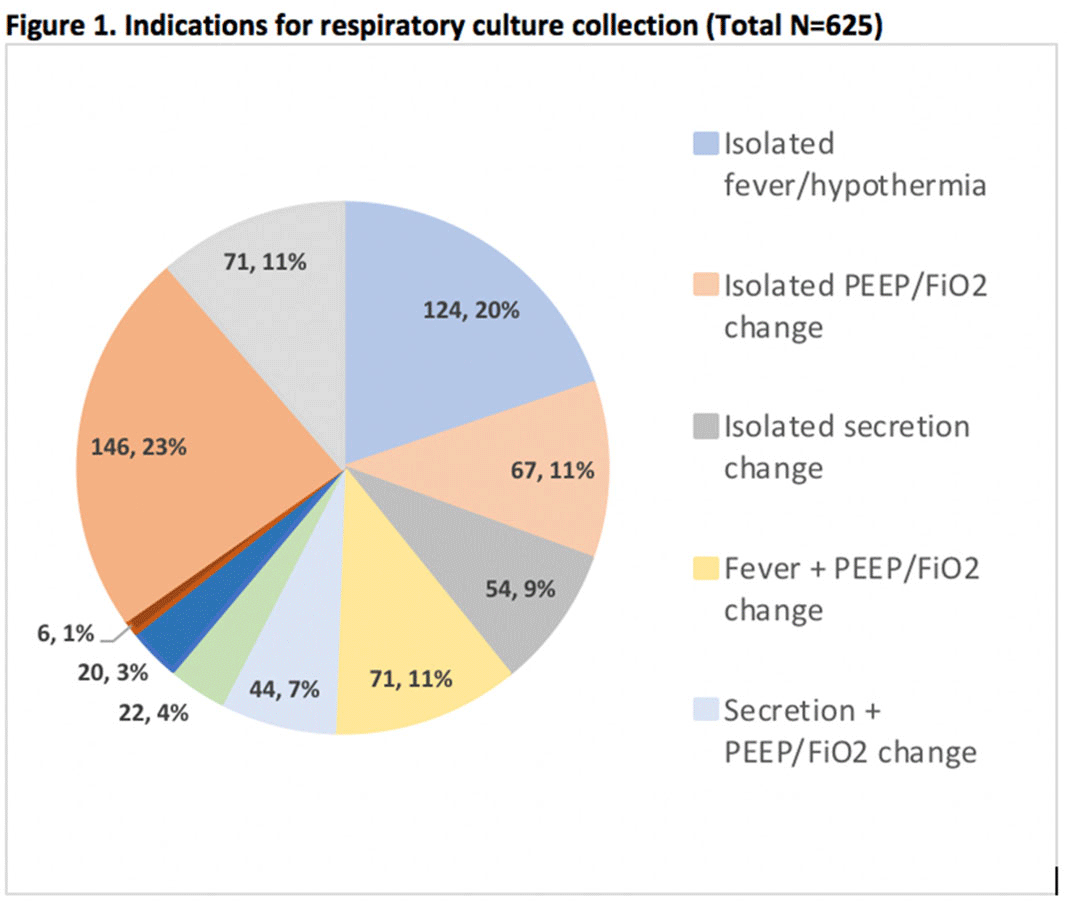
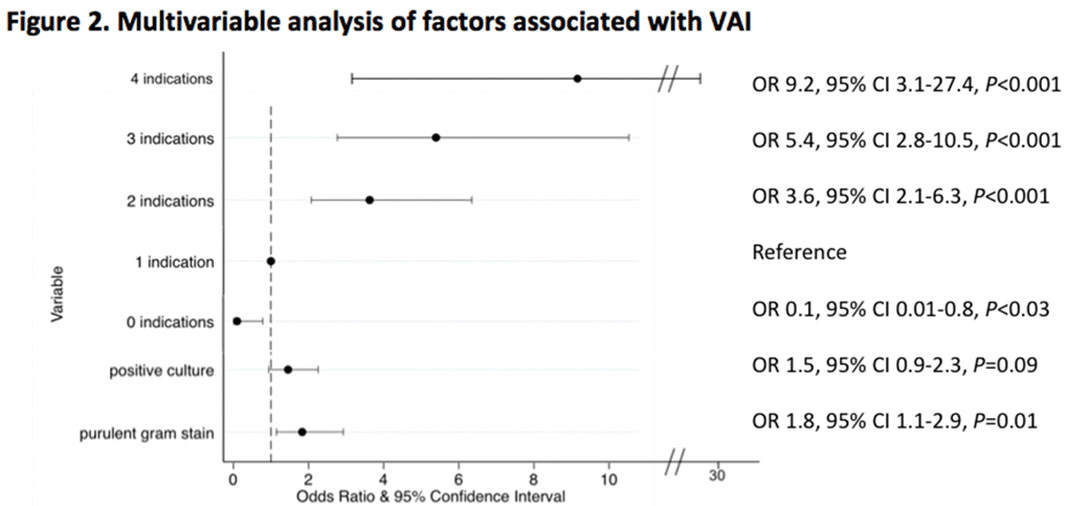
Indications for and Utility of Tracheal Aspirate Cultures for the Diagnosis of VAI
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. s60-s61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Trait attributions and threat appraisals explain why an entity theory of personality predicts greater internalizing symptoms during adolescence
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2021, pp. 1104-1114
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clinically diagnosed iron and iodine deficiencies and disorders in the entire population of US military service members from 1997 to 2015
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 11 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2021, pp. 3187-3195
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Microscopy of Polyurea Grease
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2020, pp. 12-19
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
The 4D Camera – An 87 kHz Frame-rate Detector for Counted 4D-STEM Experiments
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2020, pp. 1896-1897
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An Immunohistochemical Analysis of Free Radical Stress in the Heart of the HIV-1 Transgenic Rat
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2020, pp. 1342-1344
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation