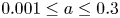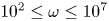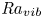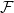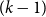417 results
Density of mode-locking property for quasi-periodically forced Arnold circle maps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-36
-
- Article
- Export citation
Application of computer vision and deep learning models to automatically classify medically important mosquitoes in North Borneo, Malaysia
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic aberrances of substantia nigra-relevant coactivation patterns in first-episode treatment-naïve patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
High propulsive performance by an oscillating foil in a stratified fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, A55
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic Adsorption of Cd2+ Onto Acid-Modified Attapulgite From Aqueous Solution
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 62 / Issue 5 / October 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 415-424
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Based on Nomogram for Predicting Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Incidence
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Distribution and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in the Ion Adsorption-type REE Deposit (IAD) at Maofeng Mountain, Guangzhou, China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 340-361
-
- Article
- Export citation
Treatment of Municipal Landfill Leachate with Organically Modified Bentonite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 518-524
-
- Article
- Export citation
Downregulated miR-150-5p in the Tissue of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Artificial Selection Drives SNPs of Olfactory Receptor Genes into Different Working Traits in Labrador Retrievers
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of antagonistic muscle actuation on the bilaminar structure of ray-finned fish in propulsion
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, A23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between the dietary antioxidant index and relative telomere length of leucocytes in the Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 1031-1040
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructural abnormalities of white matter in the cingulum bundle of adolescents with major depression and non-suicidal self-injury
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, pp. 1113-1121
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow structure transition in thermal vibrational convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, A29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Intersecting families without unique shadow
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 October 2023, pp. 91-109
-
- Article
- Export citation
Precisely constrained 134-ka strong monsoon event in the penultimate deglaciation by an annually laminated speleothem from the Asian monsoon domain
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 118 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, pp. 116-125
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thulium-doped all-PM fiber chirped pulse amplifier delivering 314 W average power
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Theoretical analysis of the effect of doping with Na(I), K(I), Mg(II), Ca(II) and Fe(II) on the electronic and mechanical properties of pyrophyllite
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, pp. 113-120
-
- Article
- Export citation
Population dynamics and conservation status of the white-headed langur in the Chongzuo forest fragments, Guangxi, China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Observations of dust fragmentations in the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2023, 175890202
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation