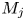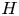254 results
Precise mode control of mid-infrared high-power laser diode using on-chip advanced sawtooth waveguide designs
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Bone-artefact production in late Neolithic central China: evidence from Pingliangtai
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Status and influencing factors of nurses’ burnout: A cross-sectional study during COVID-19 regular prevention and control in Jiangsu Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Deblending overlapping galaxies in DECaLS using Transformer-Based algorithm: a method combining multiple bands and data types
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental study on acoustic resonance of subsonic and slightly underexpanded impinging jets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 983 / 25 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, A32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Yangxin Huoxue Jiedu recipe on inflammatory factors and oxidative stress on viral myocarditis in children
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Wideband nonuniform metasurface antenna with stable gain
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Global Financialization and Local Labour Acquisition in China's Platform Economy
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Implementing a continuous quality-improvement framework for tuberculosis infection prevention and control in healthcare facilities in China, 2017–2019
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 651-657
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The importance of Righi-Leduc heat flux on the ablative Rayleigh-Taylor instability during a laser irradiating targets
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2024, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Delaminated and Pit-rich Nano-kaolinites obtained via an Intercalation-etching Method and their Application to Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 448-460
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Genesis of Kaolinitic Claystone Deposits in the Datong Coalfield, Northern China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 68-93
-
- Article
- Export citation
Part IV - Adopting Carbon Removal Mechanisms
-
- Book:
- In Pursuit of Carbon Neutrality
- Published online:
- 07 December 2023
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2023, pp 143-194
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
2 - Electricity Sector Regulation
- from Part I - Decarbonising Power Generation
-
- Book:
- In Pursuit of Carbon Neutrality
- Published online:
- 07 December 2023
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2023, pp 11-33
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - Concluding Remarks
- from Part IV - Adopting Carbon Removal Mechanisms
-
- Book:
- In Pursuit of Carbon Neutrality
- Published online:
- 07 December 2023
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2023, pp 185-194
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - Lithium and Electric Vehicles
- from Part III - Electrifying End Use
-
- Book:
- In Pursuit of Carbon Neutrality
- Published online:
- 07 December 2023
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2023, pp 122-142
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part III - Electrifying End Use
-
- Book:
- In Pursuit of Carbon Neutrality
- Published online:
- 07 December 2023
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2023, pp 99-142
-
- Chapter
- Export citation