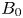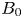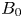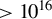835 results
Molecular-Scale Imaging of Clay Mineral Surfaces with the Atomic Force Microscope
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 38 / Issue 4 / August 1990
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 337-342
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structure and role of the pressure Hessian in regions of strong vorticity in turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 983 / 25 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, R2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P70: Development and validation study of the suicide screening questionnaire-observer rating (SSQ-OR)
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, p. 161
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Physician Management and CT Ordering in the Emergency Department for Primary Headaches
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Acceptability of self-administered antigen test for COVID-19 in the Philippines
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessing social cognition in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls using the reading the mind in the eyes test (RMET): a systematic review and meta-regression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 847-873
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal Beam Dynamics for the Heavy-Ion Synchrotron Booster Ring at HIAF
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy transfer and third-order law in forced anisotropic magneto-hydrodynamic turbulence with hyper-viscosity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, A20
-
- Article
- Export citation
The development and validation of the Discrimination and Stigma Scale Ultra Short for People Living with Dementia (DISCUS-Dementia)
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, e164
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Employees’ mindset matters: Leveraging cultural mindset to harness the benefits of organizational polyculturalism
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 408-412
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Monkeypox: a review of epidemiological modelling studies and how modelling has led to mechanistic insight
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2023, e121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An investigation of the seasonal relationships between meteorological factors, water quality, and sporadic cases of Legionnaires’ disease in Washington, DC
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, e88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
14 - Information Freshness in Large-Scale Wireless Networks: A Stochastic Geometry Approach
-
-
- Book:
- Age of Information
- Published online:
- 02 February 2023
- Print publication:
- 09 February 2023, pp 364-383
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Strain self-amplification is larger than vortex stretching due to an invariant relation of filtered velocity gradients
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 955 / 25 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2023, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effective aero-optical suppression by steady wall blowing and wall suction schemes for supersonic turbulent boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1312 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 1037-1047
-
- Article
- Export citation
A molecular dynamics study of the mechanical properties of kaolinite under uniaxial and isothermal compression at various temperatures
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2022, pp. 131-138
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of enhancing contact model on reducing family caregiving burden and improving psychological wellbeing among caregivers of persons with schizophrenia in rural China
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 5756-5766
-
- Article
- Export citation