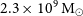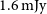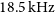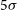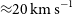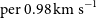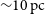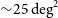176 results
Participant characteristics in the Health in Vegetarians Consortium: a collaborative analysis of 11 prospective studies
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E336
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Excessive fear of clusters of holes, its interaction with stressful life events and the association with anxiety and depressive symptoms: large epidemiological study of young people in Hong Kong
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.005 A virtual interdisciplinary diagnostic memory clinic: rural patient and caregiver satisfaction
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Use of population health data to promote equitable recruitment for a primary care practice implementation trial addressing unhealthy alcohol use
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, e110
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Childhood adversities and risk of posttraumatic stress disorder and major depression following a motor vehicle collision in adulthood
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2023, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY Pilot Survey: Public release of HI kinematic models for more than 100 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e059
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 14 - Psychological Assessment and Testing in Malaysia and Singapore
-
-
- Book:
- International Histories of Psychological Assessment
- Published online:
- 28 July 2022
- Print publication:
- 11 August 2022, pp 252-268
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Depression, anxiety and PTSD symptoms before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2022, pp. 5428-5441
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence and correlates of suicidal behaviours in a representative epidemiological youth sample in Hong Kong: the significance of suicide-related rumination, family functioning, and ongoing population-level stressors
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 10 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2022, pp. 4603-4613
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Measuring subjective stress among young people in Hong Kong: validation and predictive utility of the single-item subjective level of stress (SLS-1) in epidemiological and longitudinal community samples
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 30 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2021, e61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
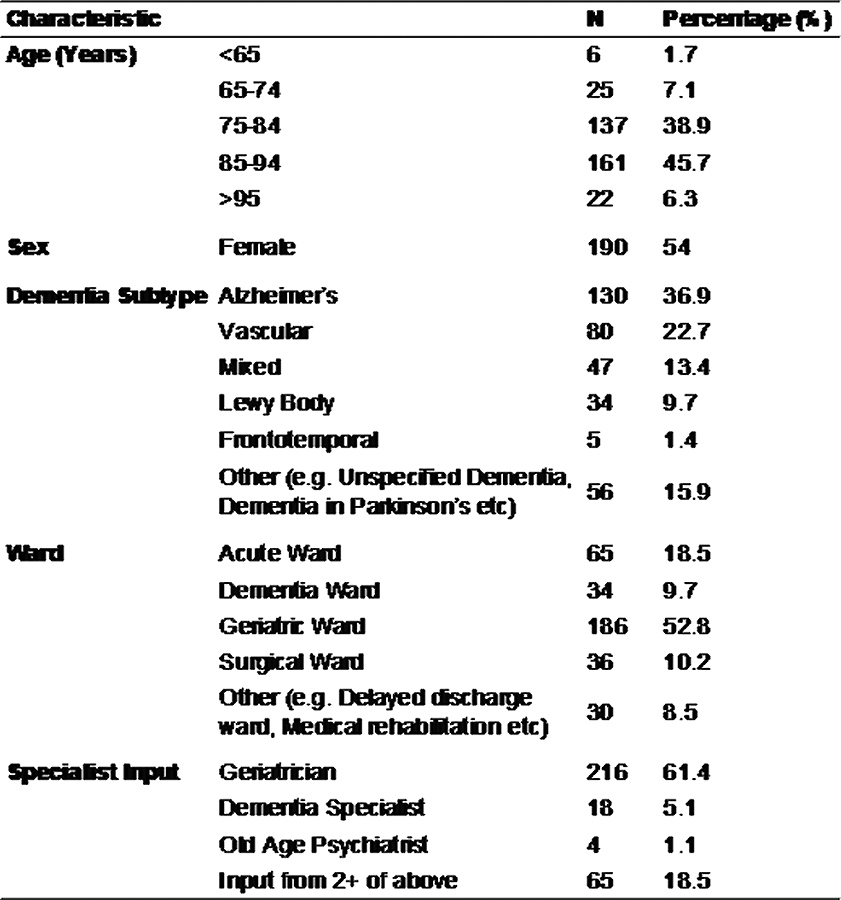
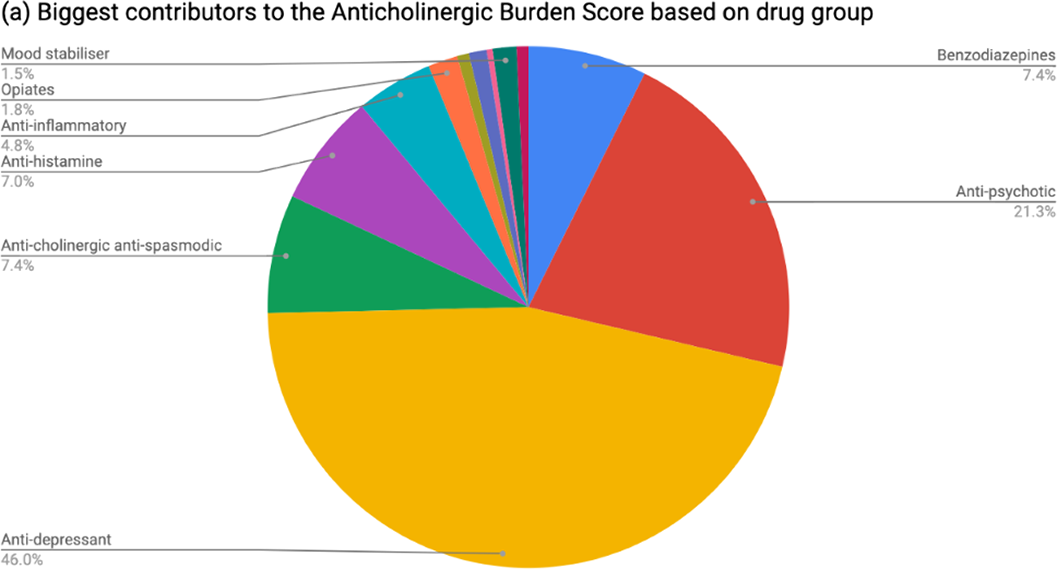
Dementia patients have greater anti-cholinergic drug burden on discharge from hospital: A multicentre cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. S422-S423
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Empowering families facing end-stage nonmalignant chronic diseases with a holistic, transdisciplinary, community-based intervention: 3 months outcome of the Life Rainbow Program – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, p. 640
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Empowering families facing end-stage nonmalignant chronic diseases with a holistic, transdisciplinary, community-based intervention: 3 months outcome of the Life Rainbow Program
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2020, pp. 530-539
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Parity and the risk of incident dementia: a COSMIC study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 29 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2020, e176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ex utero intrapartum treatment to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: lifesaving management of a giant cervical teratoma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 134 / Issue 7 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2020, pp. 650-653
- Print publication:
- July 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lower availability of midbrain serotonin transporter between healthy subjects with and without a family history of major depressive disorder – a preliminary two-ligand SPECT study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 29 / Issue 7 / September 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 414-418
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detections of far-infrared [OIII] and dust emission in a galaxy at z = 8.312: Early metal enrichment in the heart of the reionization era
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S341 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2020, pp. 211-215
- Print publication:
- November 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation