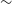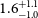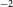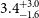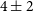201 results
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey III: Spectra and Polarisation In Cutouts of Extragalactic Sources (SPICE-RACS) first data release – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, e039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
53 2-Back Performance Does Not Differ Between Cognitive Training Groups in Older Adults Without Dementia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 360-361
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
1 Task-Based Functional Connectivity and Network Segregation of the Useful Field of View (UFOV) fMRI task
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 606-607
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
6 Adjunctive Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation and Cognitive Training Alters Default Mode and Frontoparietal Control Network Connectivity in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 675-676
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
9 Connecting memory and functional brain networks in older adults: a resting state fMRI study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 527-528
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey III: Spectra and Polarisation In Cutouts of Extragalactic Sources (SPICE-RACS) first data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, e040
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiology and preventability of hospital-onset bacteremia and fungemia in 2 hospitals in India
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2023, pp. 157-166
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
It must be awful for them: Perspective and task context affects ratings for health conditions
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 1 / Issue 2 / November 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 146-152
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Implementation of SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody Infusion Sites at Three Medical Centers in the United States: Strengths and Challenges Assessment to Inform COVID-19 Pandemic and Future Public Health Emergency Use
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2022, e112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hospital-acquired infections among adult patients admitted for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2021, pp. 1054-1057
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Australian square kilometre array pathfinder: I. system description
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Does smoking cause lower educational attainment and general cognitive ability? Triangulation of causal evidence using multiple study designs
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 8 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 1578-1586
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
18 - Genetics of Personality
- from Part IV - Biological Perspectives: Evolution, Genetics and Neuroscience of Personality
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Personality Psychology
- Published online:
- 18 September 2020
- Print publication:
- 03 September 2020, pp 247-258
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Effects of genomic copy number variants penetrant for schizophrenia on cortical thickness and surface area in healthy individuals: analysis of the UK Biobank
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 218 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. 104-111
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic liability to schizophrenia is associated with exposure to traumatic events in childhood
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 11 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2020, pp. 1814-1821
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evidence for causal effects of lifetime smoking on risk for depression and schizophrenia: a Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 14 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2019, pp. 2435-2443
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Zooarchaeological Database Preservation, Multiscalar Data Integration, and the Collaboration of the Eastern Archaic Faunal Working Group
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Archaeological Practice / Volume 7 / Issue 4 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2019, pp. 409-422
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-repetition-rate (
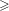 ${\geqslant}$ kHz) targets and optics from liquid microjets for high-intensity laser–plasma interactions
${\geqslant}$ kHz) targets and optics from liquid microjets for high-intensity laser–plasma interactions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2019, e50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Incidence of Clostridioides difficile infections among young and middle-aged adults: Veterans Health Administration
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 40 / Issue 9 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2019, pp. 997-1005
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation