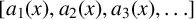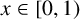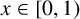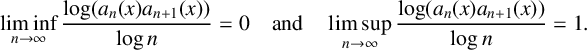37 results
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR FOR PRODUCTS OF CONSECUTIVE PARTIAL QUOTIENTS IN CONTINUED FRACTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mood disorders influencing endometriosis and adenomyosis: Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, e83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The intervention of consumer product design optimization incorporating color psychology on consumers’ anxiety disorders
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. S87-S88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Swaying motions of submerged flexible vegetation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2023, A14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of patients with SARS-COV-2 PCR re-positivity after recovering from COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review of ship collision risk assessment, hotspot detection and path planning for maritime traffic control in restricted waters
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 75 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2023, pp. 1337-1363
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tumour microenvironment: a non-negligible driver for epithelial−mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 23 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2021, e16
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the H i Content of MaNGA Major Merger Pairs
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 17 / Issue S373 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2023, pp. 186-192
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Combined protective effects of icariin and selenomethionine on novel chronic tubulointerstitial nephropathy models in vivo and in vitro
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, pp. 12-22
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Iron intake with the risk of breast cancer among Chinese women: a case–control study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 17 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2021, pp. 5743-5755
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nanostructured of SnO2/NiO composite as a highly selective formaldehyde gas sensor
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 September 2020, pp. 3079-3090
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Defending the Queen’s Pride: Effect of the menstrual cycle phase on conspicuous consumption – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology / Volume 14 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2020, e24
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Defending the Queen’s Pride: Effect of the menstrual cycle phase on conspicuous consumption
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology / Volume 14 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2020, e11
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Wisdom of Crowds reveals decline of Asian horseshoe crabs in Beibu Gulf, China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Emission properties of suprathermal electrons produced by laser–plasma interactions
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2017, pp. 663-669
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ordered porous structure of nitrogen-self-doped carbon supporting Co3O4 nanoparticles as anode for improving cycle stability in lithium-ion batteries
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 33 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2017, pp. 1226-1235
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Atomistic simulation of crack propagation in single crystal tungsten under cyclic loading
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 32 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2017, pp. 1474-1483
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molten salt synthesis of color-tunable and single-component NaY(1−x−y)(WO4)2:Eu3+ x ,Tb3+ y phosphor for UV LEDs
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 32 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2017, pp. 1548-1554
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation