Book contents
- Practical Pathology of Serous Membranes
- Practical Pathology of Serous Membranes
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- 1 The Mesothelium
- 2 Classification of Neoplastic and Non-neoplastic Lesions of the Serosal Surfaces
- 3 Multi-modality Imaging of Pleural and Peritoneal Disease
- 4 Processing of Pleural and Peritoneal Pathologic Specimens for the Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 5 Cytology of Pleural and Peritoneal Lesions
- 6 Surgical Pathology of Non-neoplastic Conditions of the Pleura, Pericardium, and Peritoneum
- 7 Surgical Pathology of Benign Lesions of Mesothelial Origin
- 8 Epidemiology, Etiology, and Pathogenesis of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 9 Pathologic “Markers” of Above Background Asbestos Exposure
- 10 Molecular Aspects of Malignant Mesothelioma and Other Tumors of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- 11 Pathology of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 12 Surgical Treatment of Pleural and Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- 13 Non-surgical Treatment of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 14 Primary Carcinoma of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- 15 Lymphoid Malignancies of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- 16 Mesenchymal and Other Unusual Tumors of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- Index
- References
1 - The Mesothelium
Embryology, Anatomy, and Biology
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 March 2018
- Practical Pathology of Serous Membranes
- Practical Pathology of Serous Membranes
- Copyright page
- Contents
- Contributors
- Preface
- 1 The Mesothelium
- 2 Classification of Neoplastic and Non-neoplastic Lesions of the Serosal Surfaces
- 3 Multi-modality Imaging of Pleural and Peritoneal Disease
- 4 Processing of Pleural and Peritoneal Pathologic Specimens for the Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 5 Cytology of Pleural and Peritoneal Lesions
- 6 Surgical Pathology of Non-neoplastic Conditions of the Pleura, Pericardium, and Peritoneum
- 7 Surgical Pathology of Benign Lesions of Mesothelial Origin
- 8 Epidemiology, Etiology, and Pathogenesis of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 9 Pathologic “Markers” of Above Background Asbestos Exposure
- 10 Molecular Aspects of Malignant Mesothelioma and Other Tumors of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- 11 Pathology of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 12 Surgical Treatment of Pleural and Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- 13 Non-surgical Treatment of Malignant Mesothelioma
- 14 Primary Carcinoma of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- 15 Lymphoid Malignancies of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- 16 Mesenchymal and Other Unusual Tumors of the Pleura and Peritoneum
- Index
- References
Summary
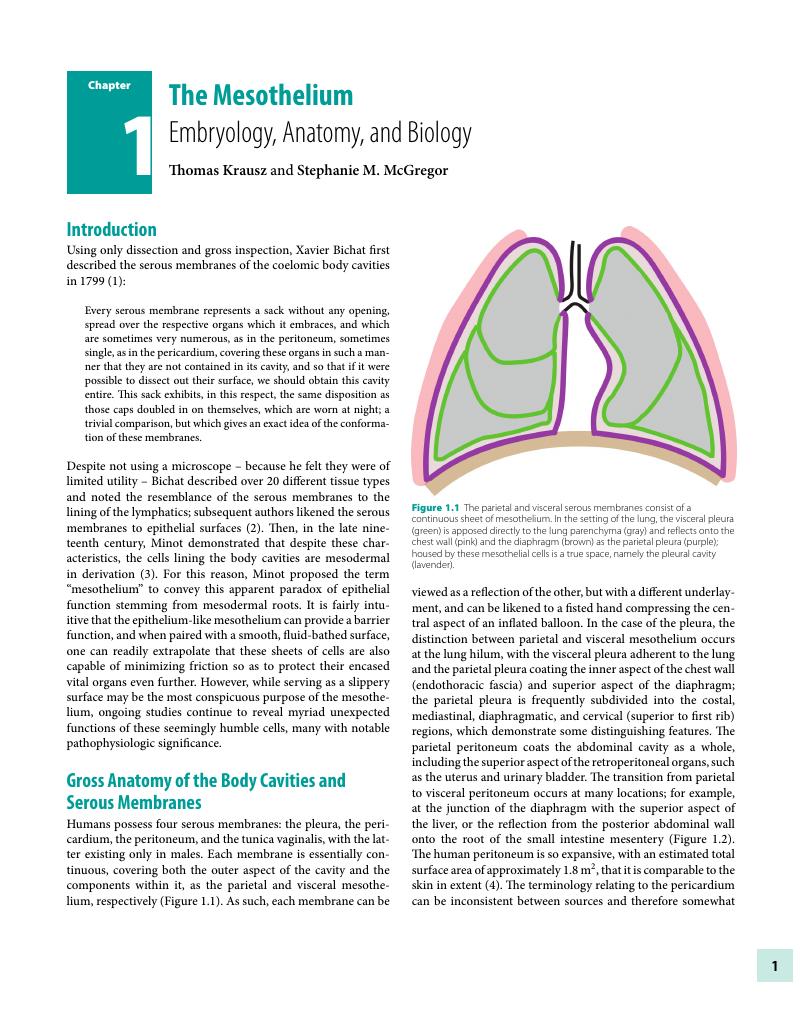
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Practical Pathology of Serous Membranes , pp. 1 - 9Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2018
References
- 2
- Cited by



