35 results
Effective aero-optical suppression by steady wall blowing and wall suction schemes for supersonic turbulent boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1312 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2022, pp. 1037-1047
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sociodemographic moderation of the association between depression and stroke incidence in a retrospective cohort of 0.4 million primary care recipients with hypertension
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 June 2020, pp. 283-291
-
- Article
- Export citation
Study of brain asymmetries in sporadic and familial first episode patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / March 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 919
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Radar absorption, basal reflection, thickness and polarization measurements from the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 61 / Issue 227 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2017, pp. 438-446
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Altered corticostriatal functional connectivity in individuals with high social anhedonia
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / January 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2015, pp. 125-135
-
- Article
- Export citation
Estimating nutrient requirements for winter oilseed rape based on QUEFTS analysis
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 154 / Issue 3 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2015, pp. 425-437
-
- Article
- Export citation
Longitudinal–transverse aerodynamic force in viscous compressible complex flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 756 / 10 October 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2014, pp. 226-251
-
- Article
- Export citation
Semi-classical bound states of Schrödinger equations
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 156 / Issue 1 / January 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2013, pp. 167-181
- Print publication:
- January 2014
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sequence variation in three mitochondrial DNA genes among isolates of Ascaridia galli originating from Guangdong, Hunan and Yunnan provinces, China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 87 / Issue 3 / September 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 October 2012, pp. 371-375
-
- Article
- Export citation
Progress and Results from the Chinese Small Telescope ARray (CSTAR)
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 8 / Issue S288 / August 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2013, pp. 231-238
- Print publication:
- August 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
EXISTENCE OF INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS FOR SUBLINEAR ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / September 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2012, pp. 535-545
- Print publication:
- September 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An epidemiological study of influenza viruses among Chinese farm families with household ducks and pigs
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 117 / Issue 1 / August 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2009, pp. 179-188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Circuit simulation of the behavior of exploding wires for nano-powder production
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / March 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2009, pp. 49-55
-
- Article
- Export citation
Disruption of Spodoptera exigua larval development by silencing chitin synthase gene A with RNA interference
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 98 / Issue 6 / December 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2008, pp. 613-619
-
- Article
- Export citation
Large third-order optical nonlinearity in Cu-doped SrBi2Nb2O9 thin films
-
- Journal:
- The European Physical Journal - Applied Physics / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / October 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2007, pp. 65-69
- Print publication:
- October 2007
-
- Article
- Export citation
Function of Centrobin: a Novel Daughter Centriole-Associated Protein
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 12 / Issue S02 / August 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 July 2006, pp. 300-301
- Print publication:
- August 2006
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Rapid and lasting increase in serine phosphorylation of rat spinal cord NMDAR1 and GluR1 subunits after peripheral inflammation
-
- Journal:
- Thalamus & Related Systems / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / March 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2005, pp. 9-18
- Print publication:
- March 2005
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural characterization and Coulomb blockade of a-SiNx/ nanocrystalline Si /a-SiNx asymmetric double-barrier structures
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 832 / 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2011, F3.6
- Print publication:
- 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation



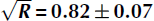 (1.7 dB reflection loss) across [0.100–0.850] GHz, and is used to correct the attenuation length. Finally, the reflected power rotated into the orthogonal antenna polarization is <5% below 0.400 GHz, compatible with air propagation. The results imply that Moore’s Bay serves as an appropriate medium for the ARIANNA high-energy neutrino detector.
(1.7 dB reflection loss) across [0.100–0.850] GHz, and is used to correct the attenuation length. Finally, the reflected power rotated into the orthogonal antenna polarization is <5% below 0.400 GHz, compatible with air propagation. The results imply that Moore’s Bay serves as an appropriate medium for the ARIANNA high-energy neutrino detector.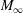
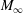
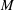
 for all
for all