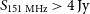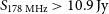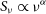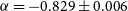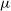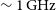102 results
1 - History-Writing and Remembrance in Crusade Letters
-
-
- Book:
- Crusade, Settlement and Historical Writing in the Latin East and Latin West, c. 1100-c. 1300
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 22 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 02 January 2024, pp 34-47
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Destigmatising mental health treatment and increasing openness to seeking treatment: randomised controlled trial of brief video interventions
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2022, e169
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Operationalising positive tipping points towards global sustainability
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 5 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A history of high-power laser research and development in the United Kingdom
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2021, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Italian Connection Reconsidered: Papal Provisions in Thirteenth-Century England
-
-
- Book:
- Thirteenth Century England XVII
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 15 December 2020
- Print publication:
- 15 January 2021, pp 147-162
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Estimating the predictive value of negative severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) results: A prospective study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 10 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 1257-1259
- Print publication:
- October 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pediatric research priorities in healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial stewardship
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 November 2020, pp. 519-522
- Print publication:
- May 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exposure to early childhood maltreatment and its effect over time on social cognition
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2020, pp. 409-419
-
- Article
- Export citation
A scale-dependent model to represent changing aerodynamic roughness of ablating glacier ice based on repeat topographic surveys
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 66 / Issue 260 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2020, pp. 950-964
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The GLEAM 4-Jy (G4Jy) Sample: I. Definition and the catalogue
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2020, e018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The GLEAM 4-Jy (G4Jy) Sample: II. Host galaxy identification for individual sources
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2020, e017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
First Crusade Letters and Medieval Monastic Scribal Cultures
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History / Volume 71 / Issue 3 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2019, pp. 484-501
- Print publication:
- July 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
5 - Diamonds and the Mantle Geodynamics of Carbon
-
-
- Book:
- Deep Carbon
- Published online:
- 03 October 2019
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2019, pp 89-128
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Equivalency of the diagnostic accuracy of the PHQ-8 and PHQ-9: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 16 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2019, p. 2816
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Equivalency of the diagnostic accuracy of the PHQ-8 and PHQ-9: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 8 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2019, pp. 1368-1380
-
- Article
- Export citation
List of Abbreviations
-
- Book:
- Petitions and Strategies of Persuasion in the Middle Ages
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 20 August 2020
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2018, pp xiii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Petitions and Strategies of Persuasion in the Middle Ages
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 20 August 2020
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2018, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - The Papacy, Petitioners and Benefices in Thirteenth-Century England
-
-
- Book:
- Petitions and Strategies of Persuasion in the Middle Ages
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 20 August 2020
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2018, pp 164-184
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Introduction: Medieval Petitions and Strategies of Persuasion
-
-
- Book:
- Petitions and Strategies of Persuasion in the Middle Ages
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 20 August 2020
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2018, pp 1-10
-
- Chapter
- Export citation