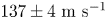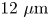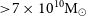76 results
Dancing ejecta
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 981 / 25 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, A4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Centering Health Equity in the Implementation of the Hospital Incident Command System: A Qualitative Case Comparison Study
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, e44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Risk of bias assessment tool for systematic review and meta-analysis of the gut microbiome
-
- Journal:
- Gut Microbiome / Volume 4 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2023, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Post-Traumatic Cognitions Inventory (PTCI): psychometric properties in clients with serious mental illness and co-occurring PTSD
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2023, pp. 459-474
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conical focusing: mechanism for singular jetting from collapsing drop-impact craters
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 958 / 10 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2023, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Variation in hospital costs and resource utilisation after congenital heart surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2022, pp. 420-431
-
- Article
- Export citation
The MAGPI survey: Science goals, design, observing strategy, early results and theoretical framework
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2021, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
What a pandemic reveals about learning in health care organizations
-
- Journal:
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology / Volume 14 / Issue 1-2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2021, pp. 126-129
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multitude of dimple shapes can produce singular jets during the collapse of immiscible drop-impact craters
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 904 / 10 December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, A19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An evaluation of direct PCR assays for the detection and quantification of Porphyromonas gingivalis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2020, e107
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P-1331 - Population-based and Family-based Association Studies of Ank3 Locus and Schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
O-64 - Blood-based Gene Expression Profiles for Classification of Subsyndromal Symptomatic Depression and Major Depressive Disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Design of Novel Deep Ultra-Violet ac-Driven Electroluminescence Devices Based on Boron Nitride nano-Materials
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 5 / Issue 8-9 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2020, pp. 421-430
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inducing Electrically-Active Defects in a Gallium Arsenide Nanowire with an Electron Beam
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 25 / Issue S2 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 1618-1619
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Gut microbiome and magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of subjects at ultra-high risk for psychosis may support the membrane hypothesis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 53 / September 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2018, pp. 37-45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
2432: A close examination of anti-retroviral drug selection and management in the optima study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2018, p. 37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Hospital-Level Variability in Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic Use for Children With Acute Leukemia Undergoing Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 39 / Issue 7 / July 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2018, pp. 797-805
- Print publication:
- July 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Follow Up of GW170817 and Its Electromagnetic Counterpart by Australian-Led Observing Programmes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 34 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2017, e069
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Suicide-related behaviours in schizophrenia in China: a comprehensive meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 28 / Issue 3 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2017, pp. 290-299
-
- Article
- Export citation